How to Convert String to Number in JavaScript?
February 9, 2024
One task that’s pretty common in JavaScript is converting strings into numbers. You’ll especially need to do it when dealing with user input or data that comes in a text format. JavaScript provides multiple ways to convert a string into a number, each with its own use case. We’ll cover them in this article.
How to useparseInt and parseFloat to convert string to a number?
The parseInt and parseFloat functions are used to convert strings to integer and floating-point numbers, respectively. parseInt will return an integer by parsing up to the first non-numeric character, while parseFloat will parse the string until it hits a character that is not part of a floating-point notation.
const integer = parseInt("123"); console.log(integer); // 123 const floatingPoint = parseFloat("123.45"); console.log(floatingPoint); // 123.45
It's important to note that parseInt also takes a second argument, the radix, which specifies the base of the number in the string. For decimal numbers, this should be 10.
const integerBaseTen = parseInt("10", 10); console.log(integerBaseTen); // 10
How to use unary plus + in JavaScript?
A quick and easy way to convert strings to numbers is by using the unary plus operator before the string. This method is concise and works well for converting a string to both integers and floating-point numbers.
const num = +"123"; console.log(num); // 123 const floatNum = +"123.45"; console.log(floatNum); // 123.45
You could ship faster.
Imagine the time you'd save if you never had to build another internal tool, write a SQL report, or manage another admin panel again. Basedash is built by internal tool builders, for internal tool builders. Our mission is to change the way developers work, so you can focus on building your product.

How to use the Number function in JS?
The Number function converts a string argument to a number. It works for both integers and floating-point numbers. If the string cannot be converted into a number, it returns NaN (Not a Number).
const num = Number("123"); console.log(num); // 123 const floatNum = Number("123.45"); console.log(floatNum); // 123.45 const notANumber = Number("abc"); console.log(notANumber); // NaN
How to useparseFloat with Number.isNaN for validation?
When you need to ensure that the conversion was successful and actually resulted in a number, you can use parseFloat in combination with Number.isNaN for validation.
const convertToNumber = (str) => { const number = parseFloat(str); if (Number.isNaN(number)) { return 'The input is not a valid number'; } return number; }; console.log(convertToNumber("123.45")); // 123.45 console.log(convertToNumber("abc")); // The input is not a valid number
Each method has its advantages depending on the specific requirements of your project. For precise control, parseInt and parseFloat are excellent, while the unary plus and Number function offer a more succinct syntax for straightforward conversions.
TOC
February 9, 2024
One task that’s pretty common in JavaScript is converting strings into numbers. You’ll especially need to do it when dealing with user input or data that comes in a text format. JavaScript provides multiple ways to convert a string into a number, each with its own use case. We’ll cover them in this article.
How to useparseInt and parseFloat to convert string to a number?
The parseInt and parseFloat functions are used to convert strings to integer and floating-point numbers, respectively. parseInt will return an integer by parsing up to the first non-numeric character, while parseFloat will parse the string until it hits a character that is not part of a floating-point notation.
const integer = parseInt("123"); console.log(integer); // 123 const floatingPoint = parseFloat("123.45"); console.log(floatingPoint); // 123.45
It's important to note that parseInt also takes a second argument, the radix, which specifies the base of the number in the string. For decimal numbers, this should be 10.
const integerBaseTen = parseInt("10", 10); console.log(integerBaseTen); // 10
How to use unary plus + in JavaScript?
A quick and easy way to convert strings to numbers is by using the unary plus operator before the string. This method is concise and works well for converting a string to both integers and floating-point numbers.
const num = +"123"; console.log(num); // 123 const floatNum = +"123.45"; console.log(floatNum); // 123.45
You could ship faster.
Imagine the time you'd save if you never had to build another internal tool, write a SQL report, or manage another admin panel again. Basedash is built by internal tool builders, for internal tool builders. Our mission is to change the way developers work, so you can focus on building your product.

How to use the Number function in JS?
The Number function converts a string argument to a number. It works for both integers and floating-point numbers. If the string cannot be converted into a number, it returns NaN (Not a Number).
const num = Number("123"); console.log(num); // 123 const floatNum = Number("123.45"); console.log(floatNum); // 123.45 const notANumber = Number("abc"); console.log(notANumber); // NaN
How to useparseFloat with Number.isNaN for validation?
When you need to ensure that the conversion was successful and actually resulted in a number, you can use parseFloat in combination with Number.isNaN for validation.
const convertToNumber = (str) => { const number = parseFloat(str); if (Number.isNaN(number)) { return 'The input is not a valid number'; } return number; }; console.log(convertToNumber("123.45")); // 123.45 console.log(convertToNumber("abc")); // The input is not a valid number
Each method has its advantages depending on the specific requirements of your project. For precise control, parseInt and parseFloat are excellent, while the unary plus and Number function offer a more succinct syntax for straightforward conversions.
February 9, 2024
One task that’s pretty common in JavaScript is converting strings into numbers. You’ll especially need to do it when dealing with user input or data that comes in a text format. JavaScript provides multiple ways to convert a string into a number, each with its own use case. We’ll cover them in this article.
How to useparseInt and parseFloat to convert string to a number?
The parseInt and parseFloat functions are used to convert strings to integer and floating-point numbers, respectively. parseInt will return an integer by parsing up to the first non-numeric character, while parseFloat will parse the string until it hits a character that is not part of a floating-point notation.
const integer = parseInt("123"); console.log(integer); // 123 const floatingPoint = parseFloat("123.45"); console.log(floatingPoint); // 123.45
It's important to note that parseInt also takes a second argument, the radix, which specifies the base of the number in the string. For decimal numbers, this should be 10.
const integerBaseTen = parseInt("10", 10); console.log(integerBaseTen); // 10
How to use unary plus + in JavaScript?
A quick and easy way to convert strings to numbers is by using the unary plus operator before the string. This method is concise and works well for converting a string to both integers and floating-point numbers.
const num = +"123"; console.log(num); // 123 const floatNum = +"123.45"; console.log(floatNum); // 123.45
You could ship faster.
Imagine the time you'd save if you never had to build another internal tool, write a SQL report, or manage another admin panel again. Basedash is built by internal tool builders, for internal tool builders. Our mission is to change the way developers work, so you can focus on building your product.

How to use the Number function in JS?
The Number function converts a string argument to a number. It works for both integers and floating-point numbers. If the string cannot be converted into a number, it returns NaN (Not a Number).
const num = Number("123"); console.log(num); // 123 const floatNum = Number("123.45"); console.log(floatNum); // 123.45 const notANumber = Number("abc"); console.log(notANumber); // NaN
How to useparseFloat with Number.isNaN for validation?
When you need to ensure that the conversion was successful and actually resulted in a number, you can use parseFloat in combination with Number.isNaN for validation.
const convertToNumber = (str) => { const number = parseFloat(str); if (Number.isNaN(number)) { return 'The input is not a valid number'; } return number; }; console.log(convertToNumber("123.45")); // 123.45 console.log(convertToNumber("abc")); // The input is not a valid number
Each method has its advantages depending on the specific requirements of your project. For precise control, parseInt and parseFloat are excellent, while the unary plus and Number function offer a more succinct syntax for straightforward conversions.
What is Basedash?
What is Basedash?
What is Basedash?
Ship faster, worry less with Basedash
Ship faster, worry less with Basedash
Ship faster, worry less with Basedash
You're busy enough with product work to be weighed down building, maintaining, scoping and developing internal apps and admin panels. Forget all of that, and give your team the admin panel that you don't have to build. Launch in less time than it takes to run a standup.
You're busy enough with product work to be weighed down building, maintaining, scoping and developing internal apps and admin panels. Forget all of that, and give your team the admin panel that you don't have to build. Launch in less time than it takes to run a standup.
You're busy enough with product work to be weighed down building, maintaining, scoping and developing internal apps and admin panels. Forget all of that, and give your team the admin panel that you don't have to build. Launch in less time than it takes to run a standup.
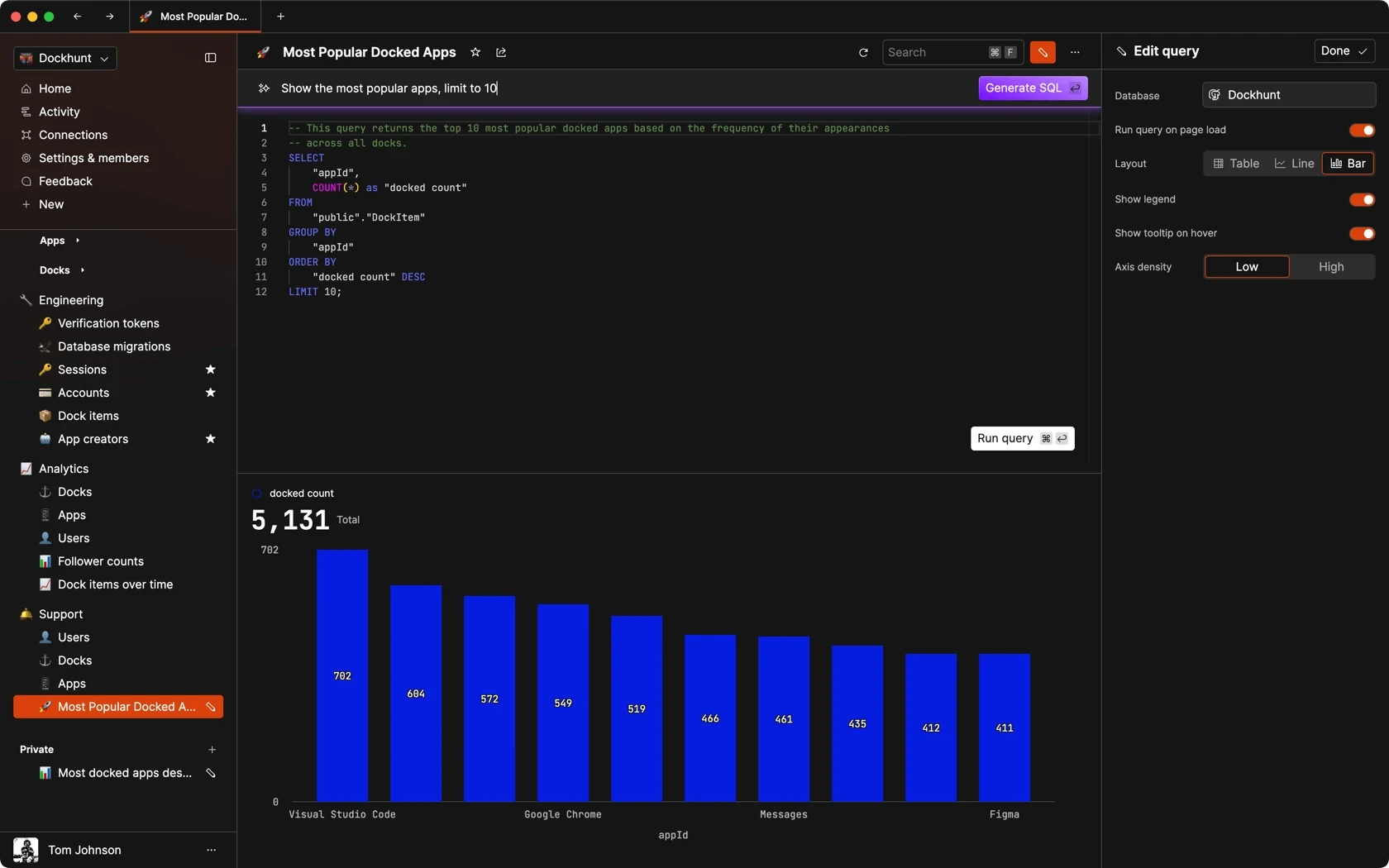
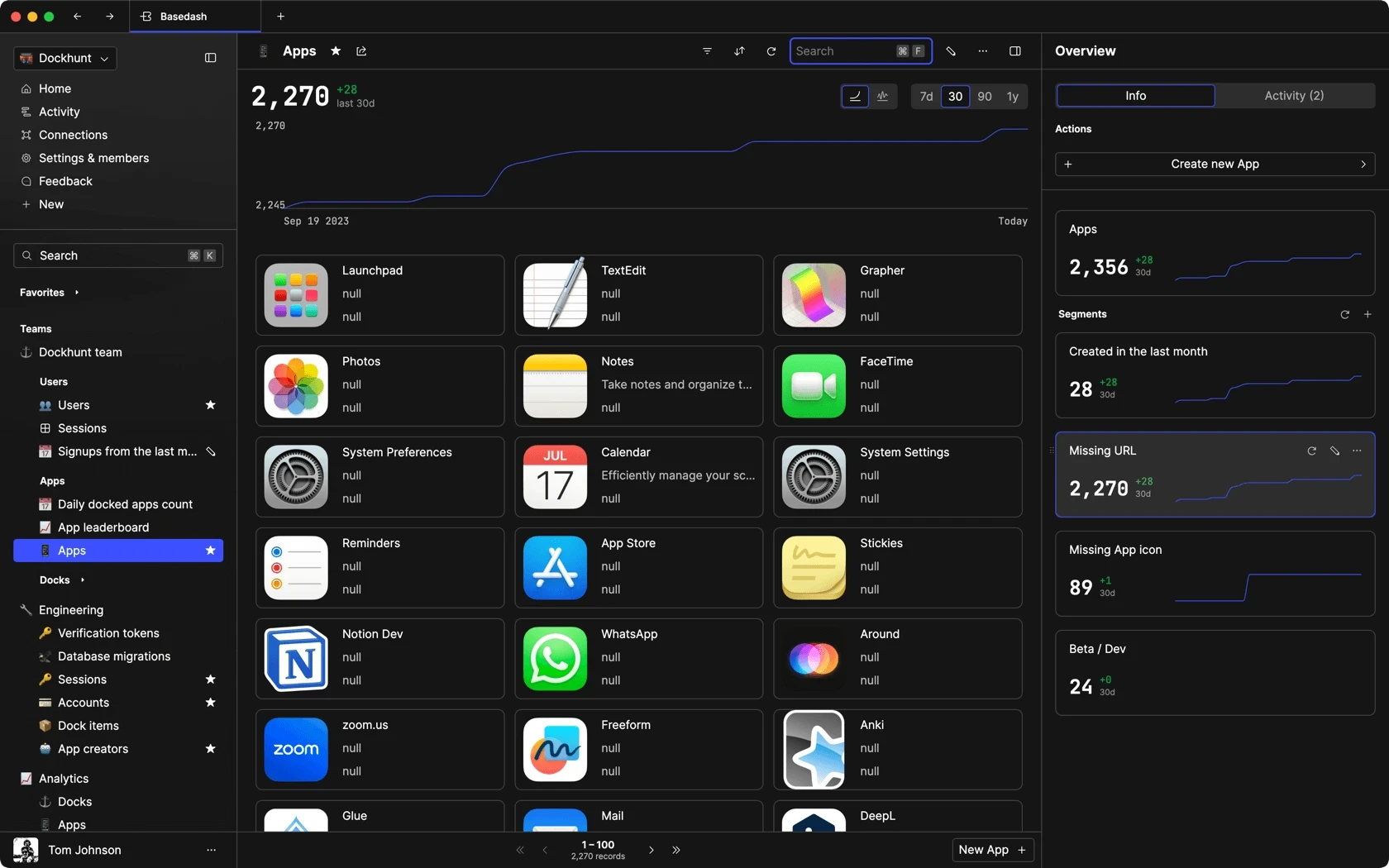
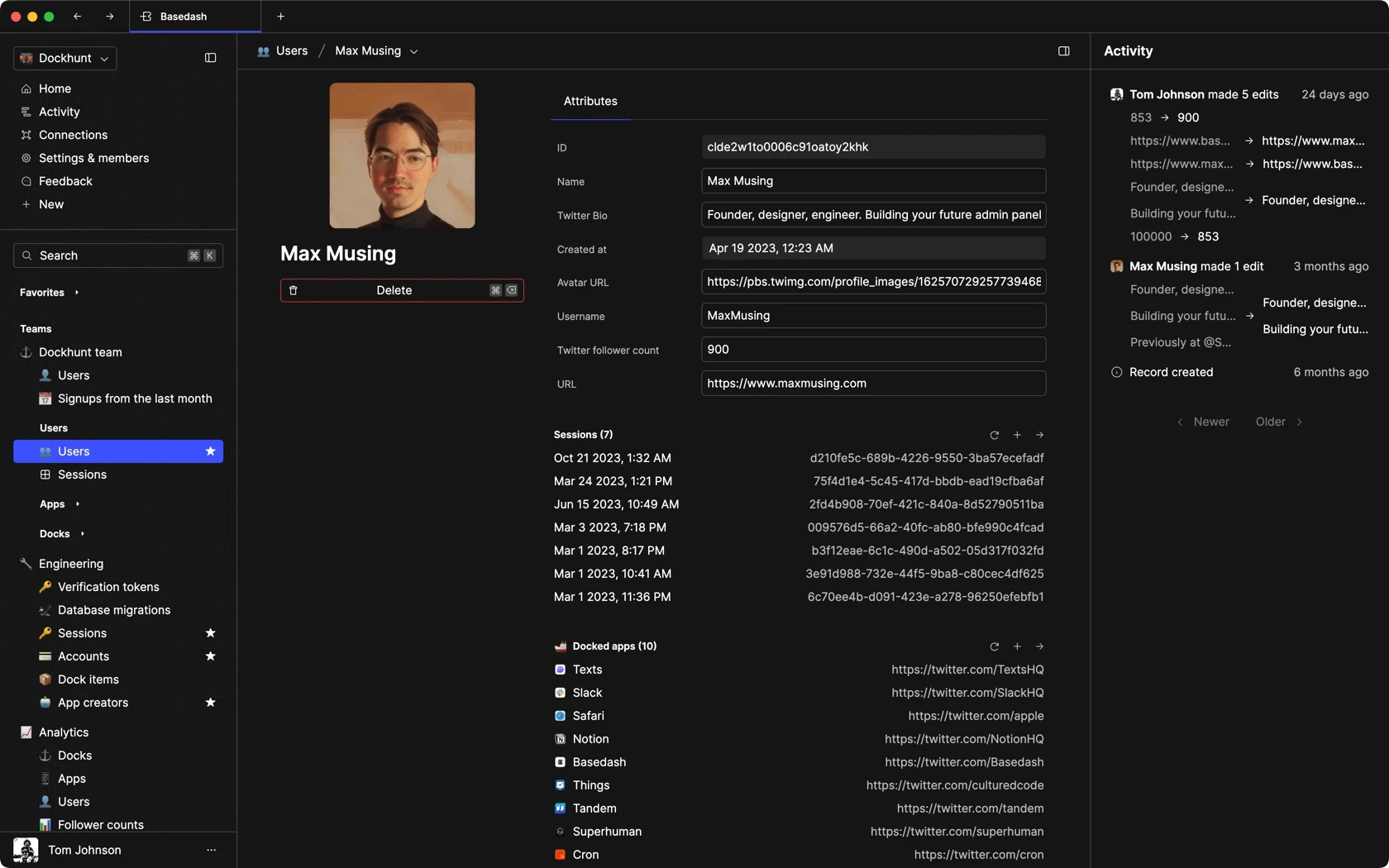
Dashboards and charts
Edit data, create records, oversee how your product is running without the need to build or manage custom software.
USER CRM
ADMIN PANEL
SQL COMPOSER WITH AI
Related posts
Related posts
Related posts



How to Remove Characters from a String in JavaScript
Jeremy Sarchet



How to Sort Strings in JavaScript
Max Musing



How to Remove Spaces from a String in JavaScript
Jeremy Sarchet



Detecting Prime Numbers in JavaScript
Robert Cooper



How to Parse Boolean Values in JavaScript
Max Musing



How to Remove a Substring from a String in JavaScript
Robert Cooper
