How to declare a multidimensional array in JavaScript
November 4, 2023
Multidimensional arrays in JavaScript are arrays whose elements are also arrays. These can be used to represent complex data structures like matrices, grids, or any other nested data configuration.
Understanding multidimensional arrays
Before delving into the syntax, it's crucial to understand that JavaScript does not have true multidimensional arrays like some other languages. Instead, we create an array of arrays. Each element of the main array (first dimension) is another array (second dimension), and this can continue for as many dimensions as needed.
Declaring a two-dimensional array
The simplest form of a multidimensional array is a two-dimensional array. It can represent a table or grid-like structure.
With array literals
Here's how to declare a two-dimensional array using array literals:
let twoDimensionalArray = [ [1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9] ];
Each inner array represents a row in the two-dimensional array.
Using a constructor
Alternatively, you can use the Array constructor to declare an empty two-dimensional array and fill it later:
let rows = 3; let cols = 3; let twoDimensionalArray = new Array(rows); for (let i = 0; i < rows; i++) { twoDimensionalArray[i] = new Array(cols); }
Declaring higher-dimensional arrays
For arrays with more than two dimensions, the concept is the same, but you add more levels of nesting.
Three-dimensional array example
Here's an example of declaring a three-dimensional array with array literals:
let threeDimensionalArray = [ [ [1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9] ], [ [10, 11, 12], [13, 14, 15], [16, 17, 18] ], [ [19, 20, 21], [22, 23, 24], [25, 26, 27] ] ];
Initializing higher dimensions dynamically
Creating higher-dimensional arrays dynamically can involve nested loops:
let depth = 3; let rows = 3; let cols = 3; let threeDimensionalArray = new Array(depth); for (let i = 0; i < depth; i++) { threeDimensionalArray[i] = new Array(rows); for (let j = 0; j < rows; j++) { threeDimensionalArray[i][j] = new Array(cols); } }
You could ship faster.
Imagine the time you'd save if you never had to build another internal tool, write a SQL report, or manage another admin panel again. Basedash is built by internal tool builders, for internal tool builders. Our mission is to change the way developers work, so you can focus on building your product.

Initializing with functions
For complex or large multidimensional arrays, initialization functions can help manage the complexity.
Function to create two-dimensional array
function create2DArray(rows, cols) { let array = new Array(rows); for (let i = 0; i < rows; i++) { array[i] = new Array(cols); } return array; } let myArray = create2DArray(3, 3);
Function to create any dimension array
For a more generic solution:
function createMultiDimensionalArray(lengths) { function createArray(lengths) { if (lengths.length === 0) { return undefined; } let length = lengths[0]; let arr = new Array(length); for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) { arr[i] = createArray(lengths.slice(1)); } return arr; } return createArray(lengths); } let myArray = createMultiDimensionalArray([3, 3, 3]);
Filling multidimensional arrays
Once declared, you can fill multidimensional arrays using loops:
for (let i = 0; i < threeDimensionalArray.length; i++) { for (let j = 0; j < threeDimensionalArray[i].length; j++) { for (let k = 0; k < threeDimensionalArray[i][j].length; k++) { threeDimensionalArray[i][j][k] = i + j + k; } } }
Tips for working with multidimensional arrays
- Consistency: Ensure all nested arrays at the same level have the same length to avoid irregular data structures.
- Access: Use multiple index brackets to access elements (e.g.,
myArray[0][1]). - Higher dimensions: Keep track of the dimensions as you nest arrays. It's easy to get lost in the brackets with more than three dimensions.
- Memory: Large multidimensional arrays can consume significant memory. Initialize only what you need.
JavaScript's flexible array structures allow for easy creation and manipulation of multidimensional arrays, as long as you keep track of the dimensions and properly manage the nested structures.
TOC
November 4, 2023
Multidimensional arrays in JavaScript are arrays whose elements are also arrays. These can be used to represent complex data structures like matrices, grids, or any other nested data configuration.
Understanding multidimensional arrays
Before delving into the syntax, it's crucial to understand that JavaScript does not have true multidimensional arrays like some other languages. Instead, we create an array of arrays. Each element of the main array (first dimension) is another array (second dimension), and this can continue for as many dimensions as needed.
Declaring a two-dimensional array
The simplest form of a multidimensional array is a two-dimensional array. It can represent a table or grid-like structure.
With array literals
Here's how to declare a two-dimensional array using array literals:
let twoDimensionalArray = [ [1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9] ];
Each inner array represents a row in the two-dimensional array.
Using a constructor
Alternatively, you can use the Array constructor to declare an empty two-dimensional array and fill it later:
let rows = 3; let cols = 3; let twoDimensionalArray = new Array(rows); for (let i = 0; i < rows; i++) { twoDimensionalArray[i] = new Array(cols); }
Declaring higher-dimensional arrays
For arrays with more than two dimensions, the concept is the same, but you add more levels of nesting.
Three-dimensional array example
Here's an example of declaring a three-dimensional array with array literals:
let threeDimensionalArray = [ [ [1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9] ], [ [10, 11, 12], [13, 14, 15], [16, 17, 18] ], [ [19, 20, 21], [22, 23, 24], [25, 26, 27] ] ];
Initializing higher dimensions dynamically
Creating higher-dimensional arrays dynamically can involve nested loops:
let depth = 3; let rows = 3; let cols = 3; let threeDimensionalArray = new Array(depth); for (let i = 0; i < depth; i++) { threeDimensionalArray[i] = new Array(rows); for (let j = 0; j < rows; j++) { threeDimensionalArray[i][j] = new Array(cols); } }
You could ship faster.
Imagine the time you'd save if you never had to build another internal tool, write a SQL report, or manage another admin panel again. Basedash is built by internal tool builders, for internal tool builders. Our mission is to change the way developers work, so you can focus on building your product.

Initializing with functions
For complex or large multidimensional arrays, initialization functions can help manage the complexity.
Function to create two-dimensional array
function create2DArray(rows, cols) { let array = new Array(rows); for (let i = 0; i < rows; i++) { array[i] = new Array(cols); } return array; } let myArray = create2DArray(3, 3);
Function to create any dimension array
For a more generic solution:
function createMultiDimensionalArray(lengths) { function createArray(lengths) { if (lengths.length === 0) { return undefined; } let length = lengths[0]; let arr = new Array(length); for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) { arr[i] = createArray(lengths.slice(1)); } return arr; } return createArray(lengths); } let myArray = createMultiDimensionalArray([3, 3, 3]);
Filling multidimensional arrays
Once declared, you can fill multidimensional arrays using loops:
for (let i = 0; i < threeDimensionalArray.length; i++) { for (let j = 0; j < threeDimensionalArray[i].length; j++) { for (let k = 0; k < threeDimensionalArray[i][j].length; k++) { threeDimensionalArray[i][j][k] = i + j + k; } } }
Tips for working with multidimensional arrays
- Consistency: Ensure all nested arrays at the same level have the same length to avoid irregular data structures.
- Access: Use multiple index brackets to access elements (e.g.,
myArray[0][1]). - Higher dimensions: Keep track of the dimensions as you nest arrays. It's easy to get lost in the brackets with more than three dimensions.
- Memory: Large multidimensional arrays can consume significant memory. Initialize only what you need.
JavaScript's flexible array structures allow for easy creation and manipulation of multidimensional arrays, as long as you keep track of the dimensions and properly manage the nested structures.
November 4, 2023
Multidimensional arrays in JavaScript are arrays whose elements are also arrays. These can be used to represent complex data structures like matrices, grids, or any other nested data configuration.
Understanding multidimensional arrays
Before delving into the syntax, it's crucial to understand that JavaScript does not have true multidimensional arrays like some other languages. Instead, we create an array of arrays. Each element of the main array (first dimension) is another array (second dimension), and this can continue for as many dimensions as needed.
Declaring a two-dimensional array
The simplest form of a multidimensional array is a two-dimensional array. It can represent a table or grid-like structure.
With array literals
Here's how to declare a two-dimensional array using array literals:
let twoDimensionalArray = [ [1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9] ];
Each inner array represents a row in the two-dimensional array.
Using a constructor
Alternatively, you can use the Array constructor to declare an empty two-dimensional array and fill it later:
let rows = 3; let cols = 3; let twoDimensionalArray = new Array(rows); for (let i = 0; i < rows; i++) { twoDimensionalArray[i] = new Array(cols); }
Declaring higher-dimensional arrays
For arrays with more than two dimensions, the concept is the same, but you add more levels of nesting.
Three-dimensional array example
Here's an example of declaring a three-dimensional array with array literals:
let threeDimensionalArray = [ [ [1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9] ], [ [10, 11, 12], [13, 14, 15], [16, 17, 18] ], [ [19, 20, 21], [22, 23, 24], [25, 26, 27] ] ];
Initializing higher dimensions dynamically
Creating higher-dimensional arrays dynamically can involve nested loops:
let depth = 3; let rows = 3; let cols = 3; let threeDimensionalArray = new Array(depth); for (let i = 0; i < depth; i++) { threeDimensionalArray[i] = new Array(rows); for (let j = 0; j < rows; j++) { threeDimensionalArray[i][j] = new Array(cols); } }
You could ship faster.
Imagine the time you'd save if you never had to build another internal tool, write a SQL report, or manage another admin panel again. Basedash is built by internal tool builders, for internal tool builders. Our mission is to change the way developers work, so you can focus on building your product.

Initializing with functions
For complex or large multidimensional arrays, initialization functions can help manage the complexity.
Function to create two-dimensional array
function create2DArray(rows, cols) { let array = new Array(rows); for (let i = 0; i < rows; i++) { array[i] = new Array(cols); } return array; } let myArray = create2DArray(3, 3);
Function to create any dimension array
For a more generic solution:
function createMultiDimensionalArray(lengths) { function createArray(lengths) { if (lengths.length === 0) { return undefined; } let length = lengths[0]; let arr = new Array(length); for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) { arr[i] = createArray(lengths.slice(1)); } return arr; } return createArray(lengths); } let myArray = createMultiDimensionalArray([3, 3, 3]);
Filling multidimensional arrays
Once declared, you can fill multidimensional arrays using loops:
for (let i = 0; i < threeDimensionalArray.length; i++) { for (let j = 0; j < threeDimensionalArray[i].length; j++) { for (let k = 0; k < threeDimensionalArray[i][j].length; k++) { threeDimensionalArray[i][j][k] = i + j + k; } } }
Tips for working with multidimensional arrays
- Consistency: Ensure all nested arrays at the same level have the same length to avoid irregular data structures.
- Access: Use multiple index brackets to access elements (e.g.,
myArray[0][1]). - Higher dimensions: Keep track of the dimensions as you nest arrays. It's easy to get lost in the brackets with more than three dimensions.
- Memory: Large multidimensional arrays can consume significant memory. Initialize only what you need.
JavaScript's flexible array structures allow for easy creation and manipulation of multidimensional arrays, as long as you keep track of the dimensions and properly manage the nested structures.
What is Basedash?
What is Basedash?
What is Basedash?
Ship faster, worry less with Basedash
Ship faster, worry less with Basedash
Ship faster, worry less with Basedash
You're busy enough with product work to be weighed down building, maintaining, scoping and developing internal apps and admin panels. Forget all of that, and give your team the admin panel that you don't have to build. Launch in less time than it takes to run a standup.
You're busy enough with product work to be weighed down building, maintaining, scoping and developing internal apps and admin panels. Forget all of that, and give your team the admin panel that you don't have to build. Launch in less time than it takes to run a standup.
You're busy enough with product work to be weighed down building, maintaining, scoping and developing internal apps and admin panels. Forget all of that, and give your team the admin panel that you don't have to build. Launch in less time than it takes to run a standup.
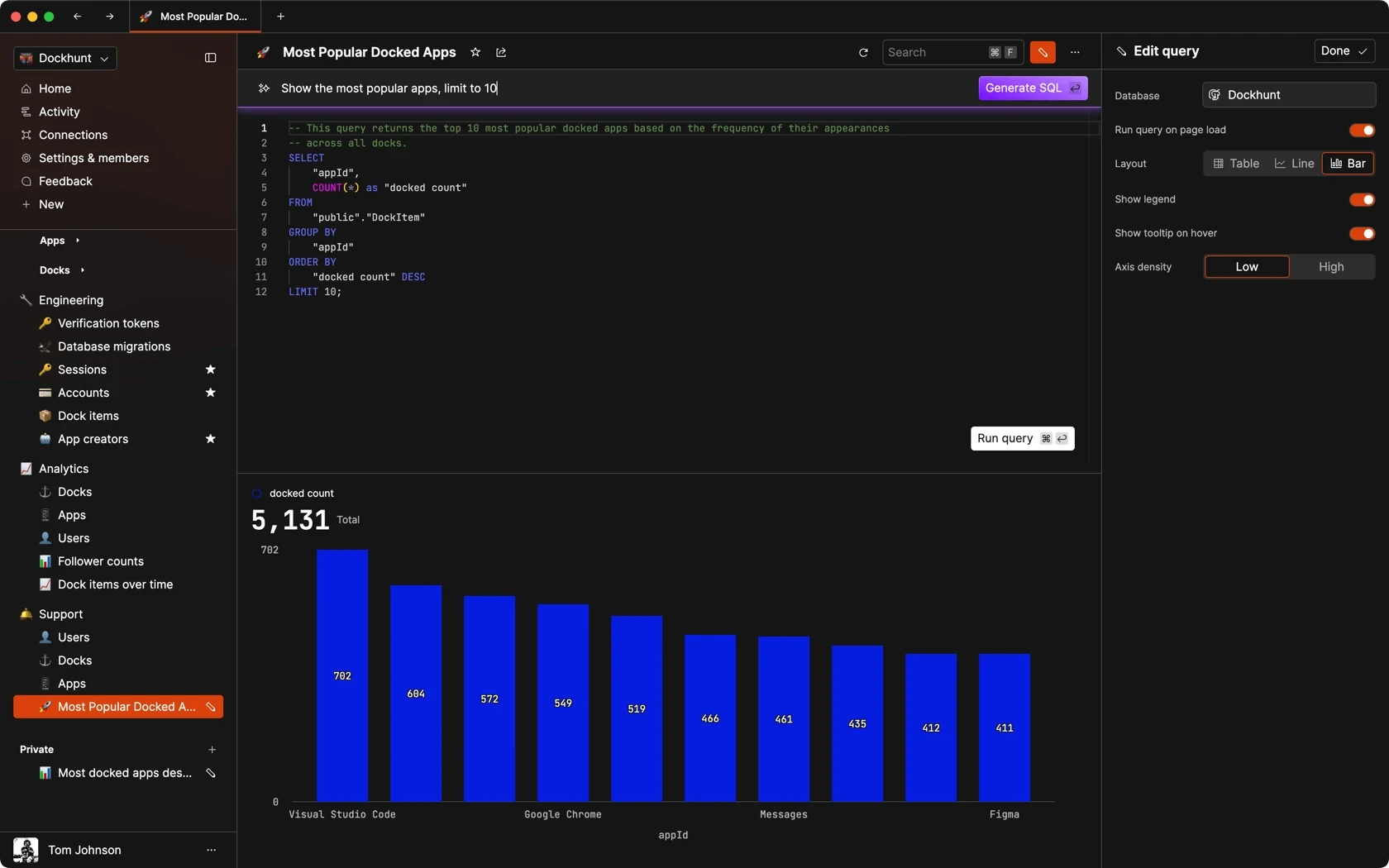
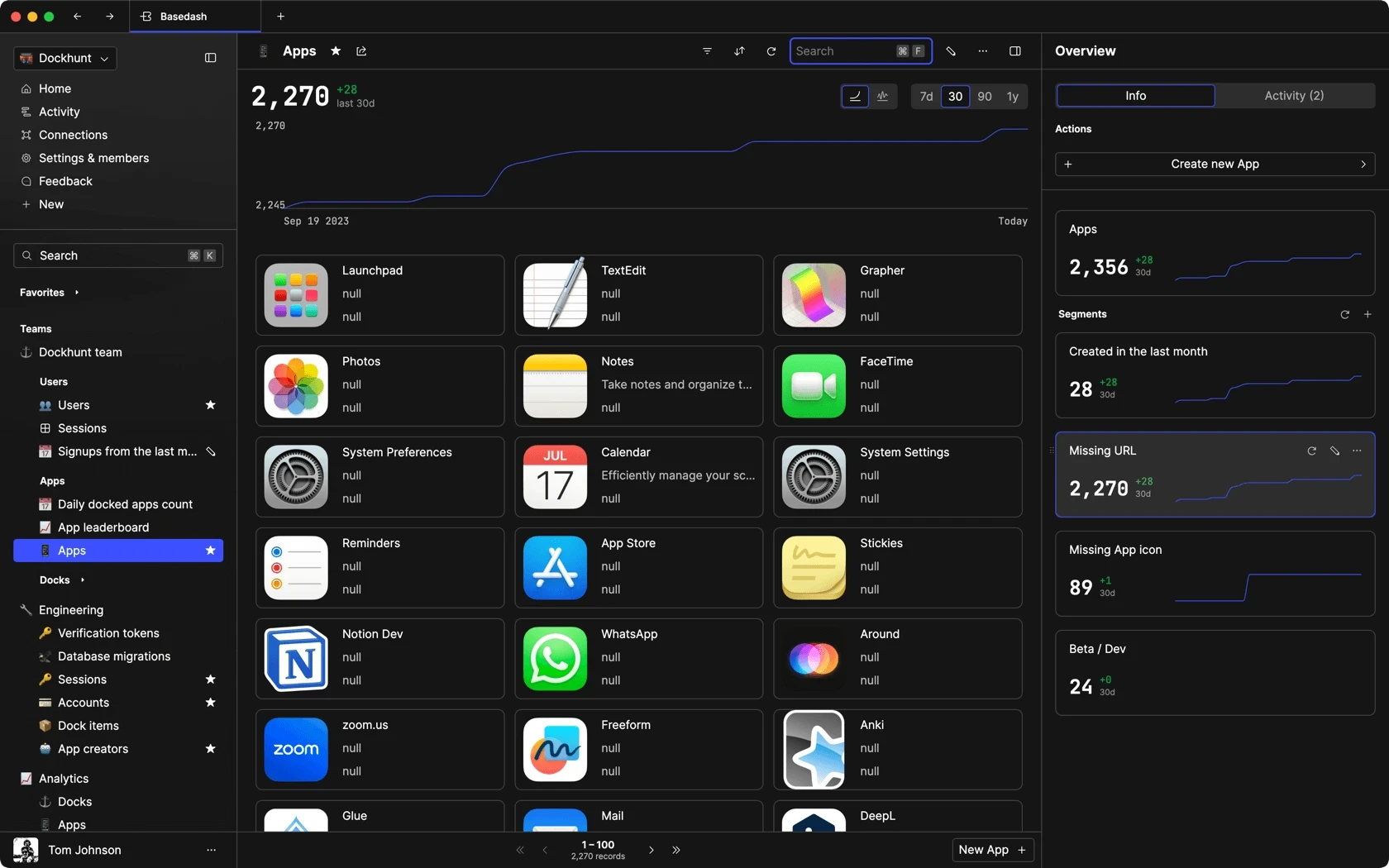
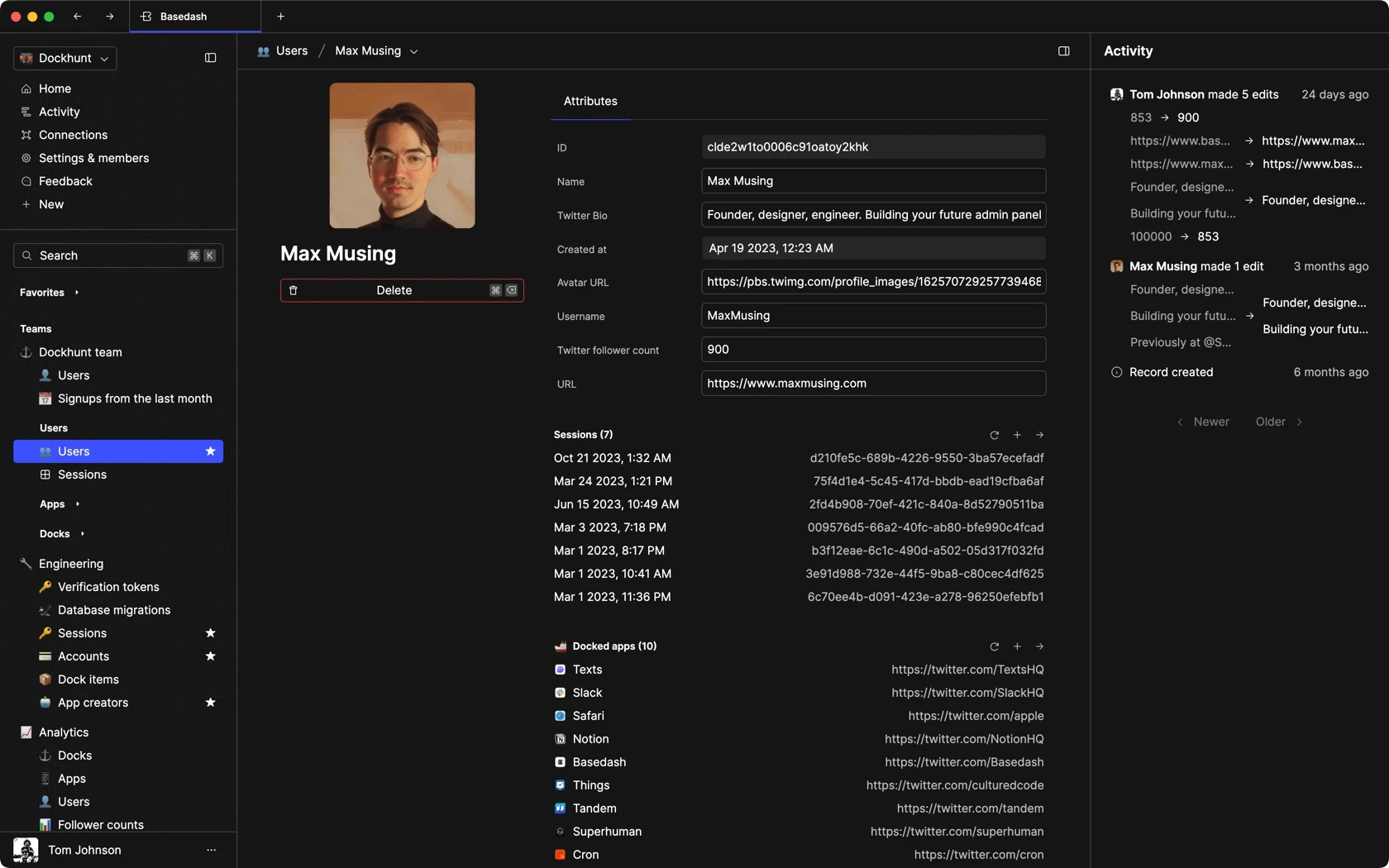
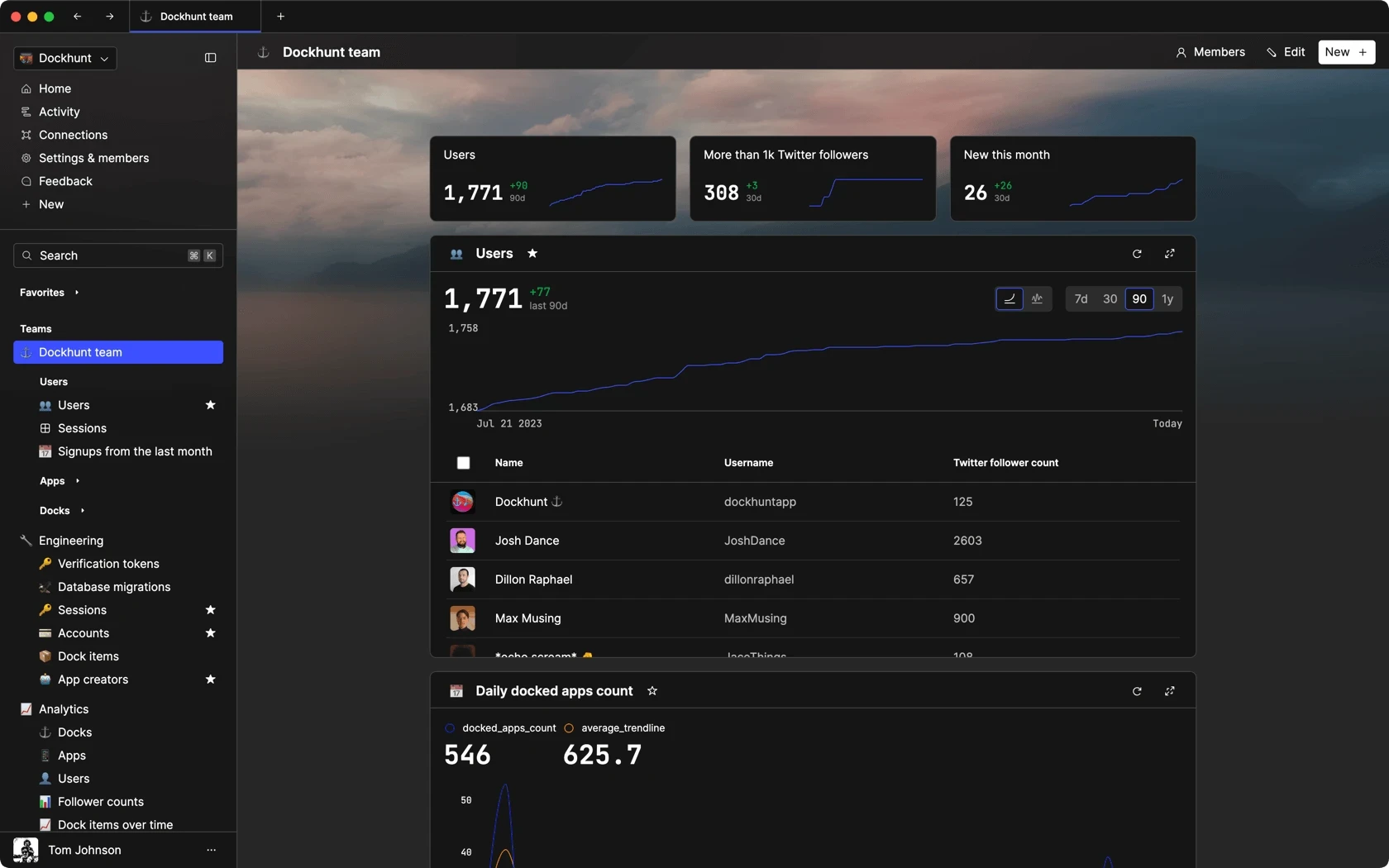
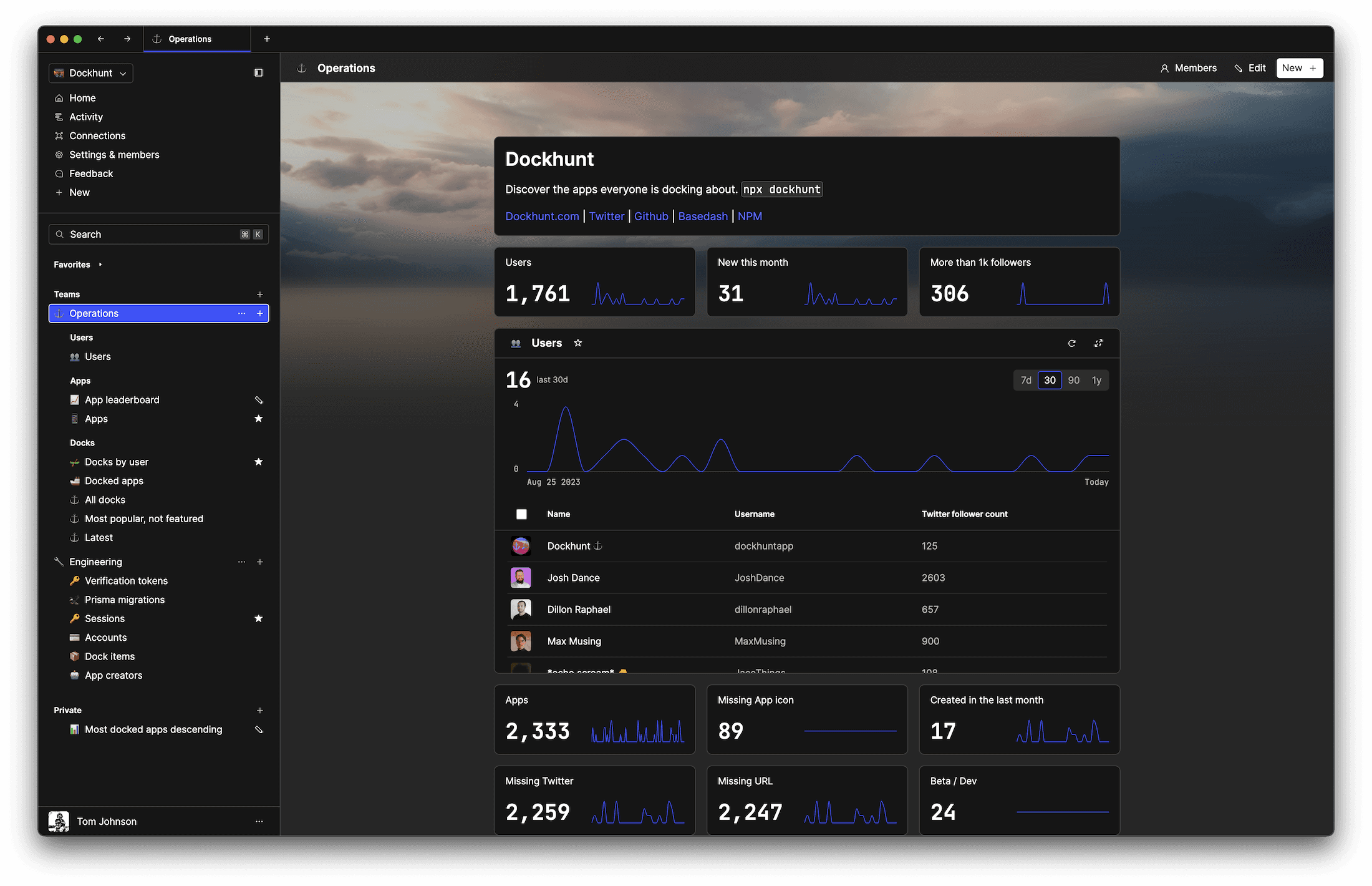
Dashboards and charts
Edit data, create records, oversee how your product is running without the need to build or manage custom software.
USER CRM
ADMIN PANEL
SQL COMPOSER WITH AI
Related posts
Related posts
Related posts



How to Remove Characters from a String in JavaScript
Jeremy Sarchet



How to Sort Strings in JavaScript
Max Musing



How to Remove Spaces from a String in JavaScript
Jeremy Sarchet



Detecting Prime Numbers in JavaScript
Robert Cooper



How to Parse Boolean Values in JavaScript
Max Musing



How to Remove a Substring from a String in JavaScript
Robert Cooper
