
How to Get Previous URL in JavaScript
November 8, 2023
Accessing the previous URL in JavaScript is a common task that involves interacting with the window object's history API. This guide provides methods to retrieve the URL that the user visited before landing on the current page.
Understanding the History API
The History API provides various properties and methods to interact with the browser history. The window.history object is key to navigating this history stack.
Retrieve the Previous URL
To get the previous URL, you can use the document.referrer property, which returns the URI of the page that linked to the current page.
const previousURL = document.referrer; console.log(previousURL);
However, document.referrer has limitations. It won't work for all scenarios, particularly if the user navigated directly to a page or if the previous site uses the rel="noreferrer" attribute.
You could ship faster.
Imagine the time you'd save if you never had to build another internal tool, write a SQL report, or manage another admin panel again. Basedash is built by internal tool builders, for internal tool builders. Our mission is to change the way developers work, so you can focus on building your product.

Using the History API
For more control over the navigation history, you can use the History API methods, like history.back(), which navigates to the previous page in the history stack.
// Navigates to the previous page, not retrieving the URL history.back();
Capturing URL During Navigation
To capture URLs as the user navigates, consider setting up event listeners that track history state changes.
window.addEventListener('popstate', function(event) { console.log('Previous URL:', event.state?.previousURL || 'No previous URL saved'); });
When changing the history state, you can store the previous URL.
history.pushState({ previousURL: window.location.href }, '', 'nextPage.html');
Conclusion
While JavaScript provides tools to interact with the browser history, it doesn't offer a direct way to retrieve the previous URL due to privacy and security reasons. document.referrer and the History API offer partial solutions, while custom state management can provide more robust tracking of navigation history.
TOC
November 8, 2023
Accessing the previous URL in JavaScript is a common task that involves interacting with the window object's history API. This guide provides methods to retrieve the URL that the user visited before landing on the current page.
Understanding the History API
The History API provides various properties and methods to interact with the browser history. The window.history object is key to navigating this history stack.
Retrieve the Previous URL
To get the previous URL, you can use the document.referrer property, which returns the URI of the page that linked to the current page.
const previousURL = document.referrer; console.log(previousURL);
However, document.referrer has limitations. It won't work for all scenarios, particularly if the user navigated directly to a page or if the previous site uses the rel="noreferrer" attribute.
You could ship faster.
Imagine the time you'd save if you never had to build another internal tool, write a SQL report, or manage another admin panel again. Basedash is built by internal tool builders, for internal tool builders. Our mission is to change the way developers work, so you can focus on building your product.

Using the History API
For more control over the navigation history, you can use the History API methods, like history.back(), which navigates to the previous page in the history stack.
// Navigates to the previous page, not retrieving the URL history.back();
Capturing URL During Navigation
To capture URLs as the user navigates, consider setting up event listeners that track history state changes.
window.addEventListener('popstate', function(event) { console.log('Previous URL:', event.state?.previousURL || 'No previous URL saved'); });
When changing the history state, you can store the previous URL.
history.pushState({ previousURL: window.location.href }, '', 'nextPage.html');
Conclusion
While JavaScript provides tools to interact with the browser history, it doesn't offer a direct way to retrieve the previous URL due to privacy and security reasons. document.referrer and the History API offer partial solutions, while custom state management can provide more robust tracking of navigation history.
November 8, 2023
Accessing the previous URL in JavaScript is a common task that involves interacting with the window object's history API. This guide provides methods to retrieve the URL that the user visited before landing on the current page.
Understanding the History API
The History API provides various properties and methods to interact with the browser history. The window.history object is key to navigating this history stack.
Retrieve the Previous URL
To get the previous URL, you can use the document.referrer property, which returns the URI of the page that linked to the current page.
const previousURL = document.referrer; console.log(previousURL);
However, document.referrer has limitations. It won't work for all scenarios, particularly if the user navigated directly to a page or if the previous site uses the rel="noreferrer" attribute.
You could ship faster.
Imagine the time you'd save if you never had to build another internal tool, write a SQL report, or manage another admin panel again. Basedash is built by internal tool builders, for internal tool builders. Our mission is to change the way developers work, so you can focus on building your product.

Using the History API
For more control over the navigation history, you can use the History API methods, like history.back(), which navigates to the previous page in the history stack.
// Navigates to the previous page, not retrieving the URL history.back();
Capturing URL During Navigation
To capture URLs as the user navigates, consider setting up event listeners that track history state changes.
window.addEventListener('popstate', function(event) { console.log('Previous URL:', event.state?.previousURL || 'No previous URL saved'); });
When changing the history state, you can store the previous URL.
history.pushState({ previousURL: window.location.href }, '', 'nextPage.html');
Conclusion
While JavaScript provides tools to interact with the browser history, it doesn't offer a direct way to retrieve the previous URL due to privacy and security reasons. document.referrer and the History API offer partial solutions, while custom state management can provide more robust tracking of navigation history.
What is Basedash?
What is Basedash?
What is Basedash?
Ship faster, worry less with Basedash
Ship faster, worry less with Basedash
Ship faster, worry less with Basedash
You're busy enough with product work to be weighed down building, maintaining, scoping and developing internal apps and admin panels. Forget all of that, and give your team the admin panel that you don't have to build. Launch in less time than it takes to run a standup.
You're busy enough with product work to be weighed down building, maintaining, scoping and developing internal apps and admin panels. Forget all of that, and give your team the admin panel that you don't have to build. Launch in less time than it takes to run a standup.
You're busy enough with product work to be weighed down building, maintaining, scoping and developing internal apps and admin panels. Forget all of that, and give your team the admin panel that you don't have to build. Launch in less time than it takes to run a standup.
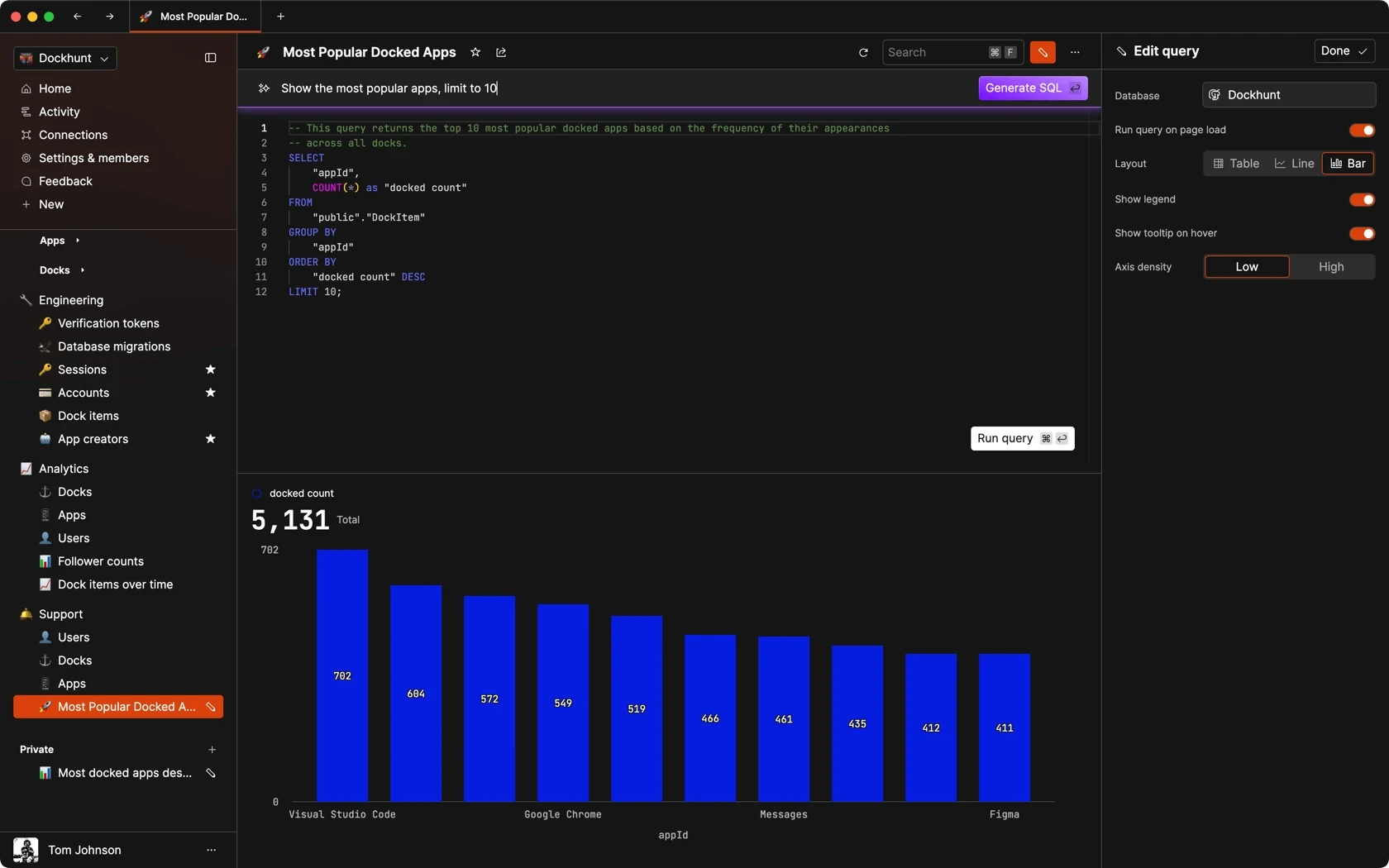
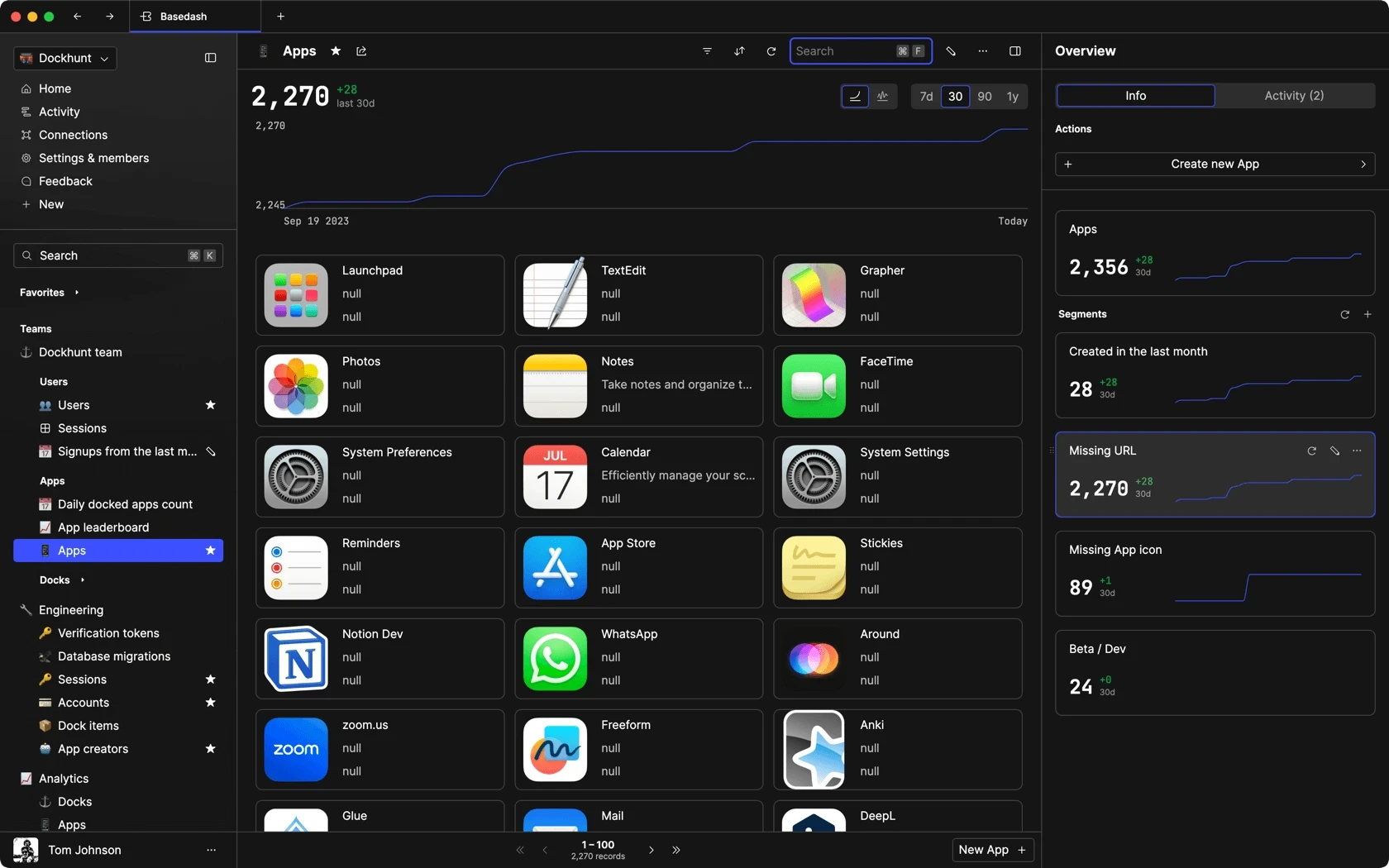
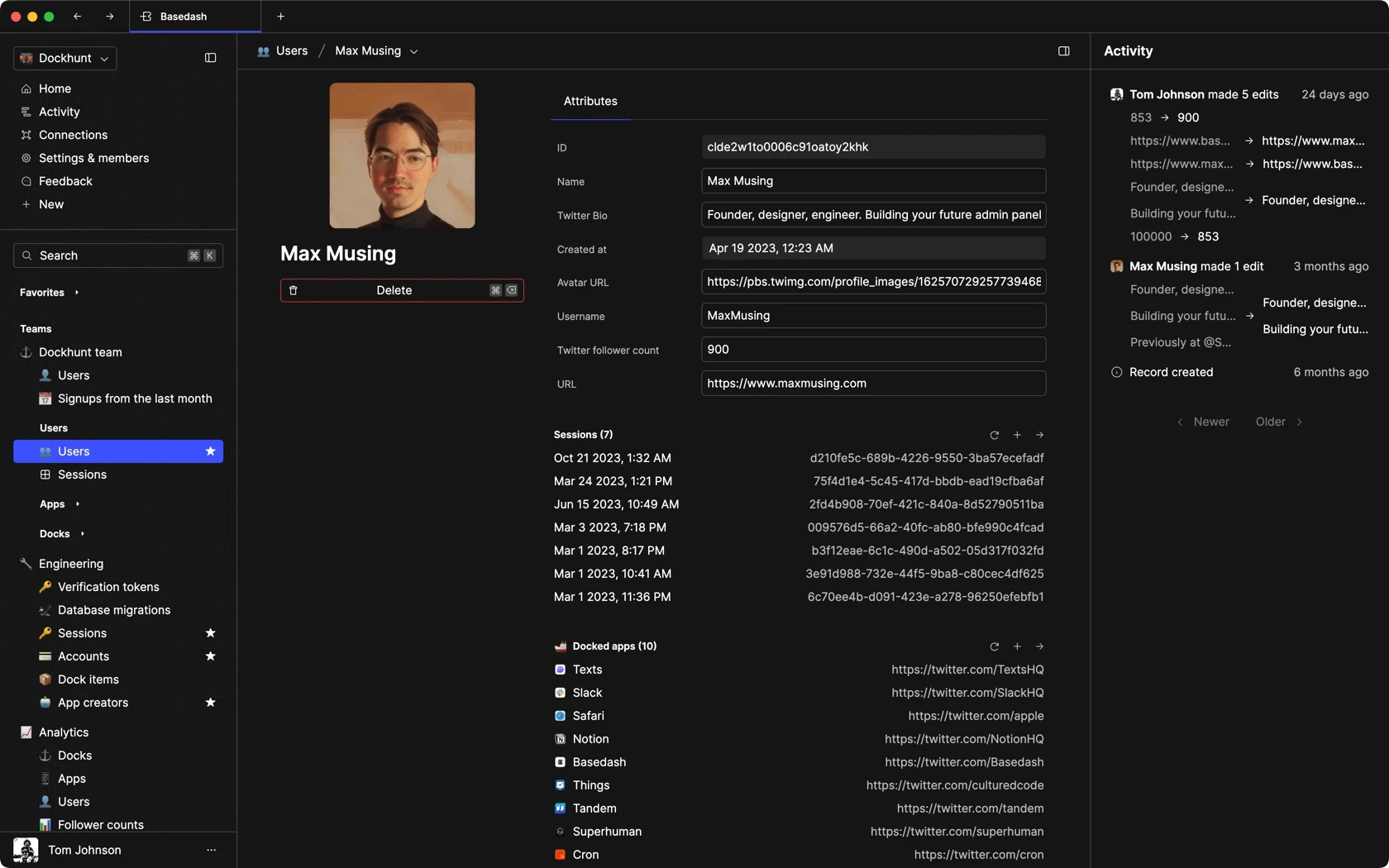
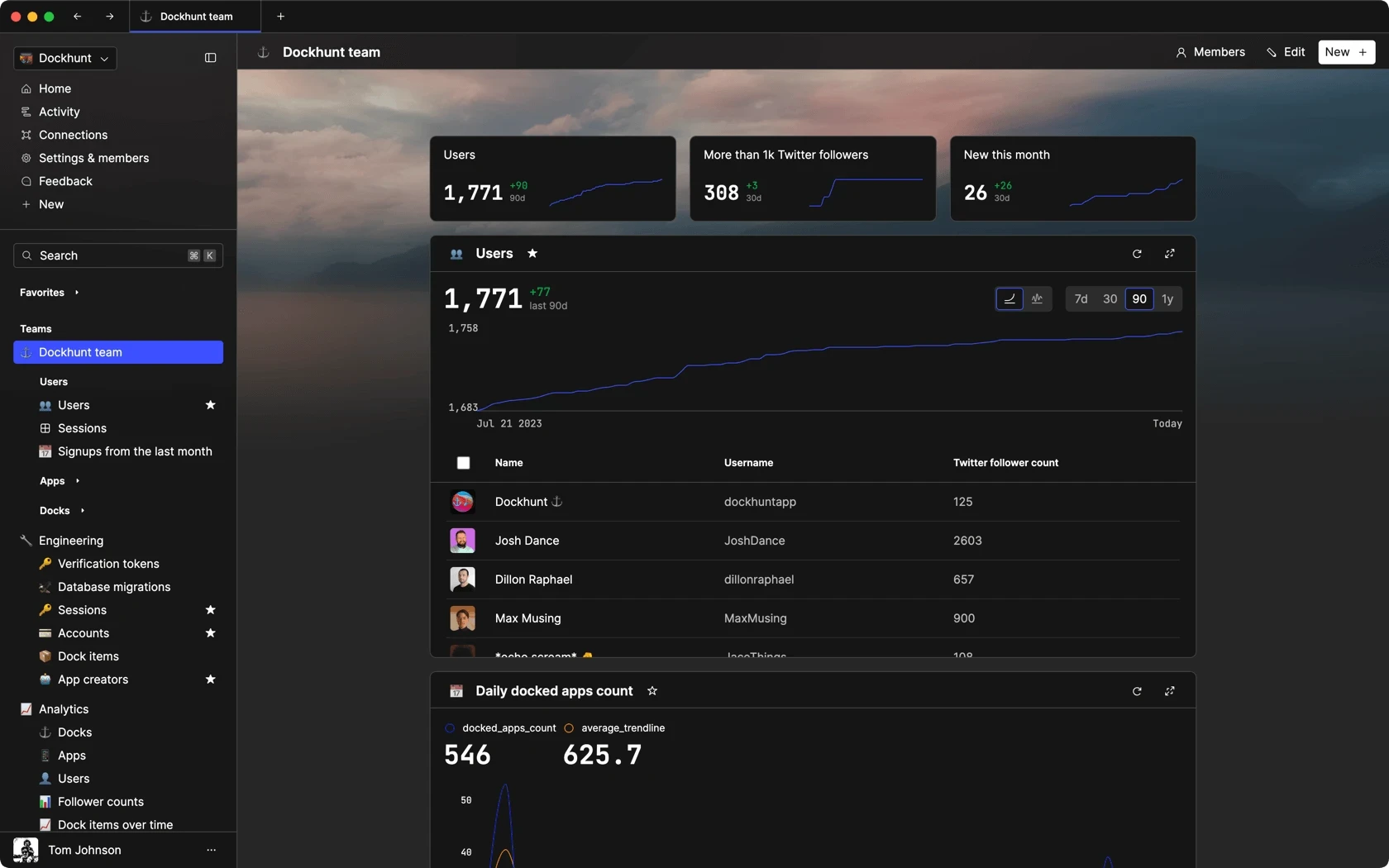
Dashboards and charts
Edit data, create records, oversee how your product is running without the need to build or manage custom software.
USER CRM
ADMIN PANEL
SQL COMPOSER WITH AI
Related posts
Related posts
Related posts



How to Remove Characters from a String in JavaScript
Jeremy Sarchet



How to Sort Strings in JavaScript
Max Musing



How to Remove Spaces from a String in JavaScript
Jeremy Sarchet



Detecting Prime Numbers in JavaScript
Robert Cooper



How to Parse Boolean Values in JavaScript
Max Musing



How to Remove a Substring from a String in JavaScript
Robert Cooper
