
How to rename a file in JavaScript
November 8, 2023
Renaming a file in JavaScript typically involves the manipulation of file system paths within a server-side environment like Node.js, since client-side JavaScript in the browser does not have the permission to directly rename files on the filesystem. The Node.js fs module, which provides an API for interacting with the file system, is essential for this operation.
Understanding the fs module
The fs module includes the fs.rename() method used to asynchronously rename a file at the path specified.
const fs = require('fs'); fs.rename('/path/to/current/file', '/path/to/new/file', (err) => { if (err) throw err; console.log('Rename complete!'); });
Synchronous file renaming
For synchronous renaming, use fs.renameSync() method. It blocks the Node.js event loop until the file is renamed.
const fs = require('fs'); try { fs.renameSync('/path/to/current/file', '/path/to/new/file'); console.log('Rename complete!'); } catch (err) { throw err; }
Renaming with promises
Node.js also allows you to use promises with the fs.promises API for a cleaner asynchronous code structure.
const fs = require('fs').promises; async function renameFile(oldPath, newPath) { try { await fs.rename(oldPath, newPath); console.log('Rename complete!'); } catch (err) { throw err; } } renameFile('/path/to/current/file', '/path/to/new/file');
You could ship faster.
Imagine the time you'd save if you never had to build another internal tool, write a SQL report, or manage another admin panel again. Basedash is built by internal tool builders, for internal tool builders. Our mission is to change the way developers work, so you can focus on building your product.

Error handling
It is crucial to handle errors effectively to avoid crashing your application. Use try/catch blocks for synchronous code, and for asynchronous code, make sure to handle promise rejections.
const fs = require('fs').promises; async function renameFile(oldPath, newPath) { try { await fs.rename(oldPath, newPath); console.log('Rename complete!'); } catch (err) { console.error('Error occurred:', err); } } renameFile('/path/to/current/file', '/path/to/new/file');
Using fs with async/await
For a modern approach, integrating async/await syntax with fs.promises can lead to more readable code.
const fs = require('fs').promises; async function renameFile() { try { await fs.rename('/path/to/current/file', '/path/to/new/file'); console.log('Rename operation successful'); } catch (error) { console.error('Error during renaming:', error.message); } } renameFile();
File renaming in a web browser
If you need to rename a file within a web browser context, for example when dealing with files in an input element, you can't directly rename the file, but you can create a new File object with the desired name.
const fileInput = document.querySelector('input[type="file"]'); fileInput.addEventListener('change', (event) => { const file = event.target.files[0]; const newFile = new File([file], 'newFileName.txt', { type: file.type }); // Now you can upload 'newFile' using FormData or other methods });
By following these patterns, you can effectively rename files in a Node.js environment or manipulate file references in a web browser context.
TOC
November 8, 2023
Renaming a file in JavaScript typically involves the manipulation of file system paths within a server-side environment like Node.js, since client-side JavaScript in the browser does not have the permission to directly rename files on the filesystem. The Node.js fs module, which provides an API for interacting with the file system, is essential for this operation.
Understanding the fs module
The fs module includes the fs.rename() method used to asynchronously rename a file at the path specified.
const fs = require('fs'); fs.rename('/path/to/current/file', '/path/to/new/file', (err) => { if (err) throw err; console.log('Rename complete!'); });
Synchronous file renaming
For synchronous renaming, use fs.renameSync() method. It blocks the Node.js event loop until the file is renamed.
const fs = require('fs'); try { fs.renameSync('/path/to/current/file', '/path/to/new/file'); console.log('Rename complete!'); } catch (err) { throw err; }
Renaming with promises
Node.js also allows you to use promises with the fs.promises API for a cleaner asynchronous code structure.
const fs = require('fs').promises; async function renameFile(oldPath, newPath) { try { await fs.rename(oldPath, newPath); console.log('Rename complete!'); } catch (err) { throw err; } } renameFile('/path/to/current/file', '/path/to/new/file');
You could ship faster.
Imagine the time you'd save if you never had to build another internal tool, write a SQL report, or manage another admin panel again. Basedash is built by internal tool builders, for internal tool builders. Our mission is to change the way developers work, so you can focus on building your product.

Error handling
It is crucial to handle errors effectively to avoid crashing your application. Use try/catch blocks for synchronous code, and for asynchronous code, make sure to handle promise rejections.
const fs = require('fs').promises; async function renameFile(oldPath, newPath) { try { await fs.rename(oldPath, newPath); console.log('Rename complete!'); } catch (err) { console.error('Error occurred:', err); } } renameFile('/path/to/current/file', '/path/to/new/file');
Using fs with async/await
For a modern approach, integrating async/await syntax with fs.promises can lead to more readable code.
const fs = require('fs').promises; async function renameFile() { try { await fs.rename('/path/to/current/file', '/path/to/new/file'); console.log('Rename operation successful'); } catch (error) { console.error('Error during renaming:', error.message); } } renameFile();
File renaming in a web browser
If you need to rename a file within a web browser context, for example when dealing with files in an input element, you can't directly rename the file, but you can create a new File object with the desired name.
const fileInput = document.querySelector('input[type="file"]'); fileInput.addEventListener('change', (event) => { const file = event.target.files[0]; const newFile = new File([file], 'newFileName.txt', { type: file.type }); // Now you can upload 'newFile' using FormData or other methods });
By following these patterns, you can effectively rename files in a Node.js environment or manipulate file references in a web browser context.
November 8, 2023
Renaming a file in JavaScript typically involves the manipulation of file system paths within a server-side environment like Node.js, since client-side JavaScript in the browser does not have the permission to directly rename files on the filesystem. The Node.js fs module, which provides an API for interacting with the file system, is essential for this operation.
Understanding the fs module
The fs module includes the fs.rename() method used to asynchronously rename a file at the path specified.
const fs = require('fs'); fs.rename('/path/to/current/file', '/path/to/new/file', (err) => { if (err) throw err; console.log('Rename complete!'); });
Synchronous file renaming
For synchronous renaming, use fs.renameSync() method. It blocks the Node.js event loop until the file is renamed.
const fs = require('fs'); try { fs.renameSync('/path/to/current/file', '/path/to/new/file'); console.log('Rename complete!'); } catch (err) { throw err; }
Renaming with promises
Node.js also allows you to use promises with the fs.promises API for a cleaner asynchronous code structure.
const fs = require('fs').promises; async function renameFile(oldPath, newPath) { try { await fs.rename(oldPath, newPath); console.log('Rename complete!'); } catch (err) { throw err; } } renameFile('/path/to/current/file', '/path/to/new/file');
You could ship faster.
Imagine the time you'd save if you never had to build another internal tool, write a SQL report, or manage another admin panel again. Basedash is built by internal tool builders, for internal tool builders. Our mission is to change the way developers work, so you can focus on building your product.

Error handling
It is crucial to handle errors effectively to avoid crashing your application. Use try/catch blocks for synchronous code, and for asynchronous code, make sure to handle promise rejections.
const fs = require('fs').promises; async function renameFile(oldPath, newPath) { try { await fs.rename(oldPath, newPath); console.log('Rename complete!'); } catch (err) { console.error('Error occurred:', err); } } renameFile('/path/to/current/file', '/path/to/new/file');
Using fs with async/await
For a modern approach, integrating async/await syntax with fs.promises can lead to more readable code.
const fs = require('fs').promises; async function renameFile() { try { await fs.rename('/path/to/current/file', '/path/to/new/file'); console.log('Rename operation successful'); } catch (error) { console.error('Error during renaming:', error.message); } } renameFile();
File renaming in a web browser
If you need to rename a file within a web browser context, for example when dealing with files in an input element, you can't directly rename the file, but you can create a new File object with the desired name.
const fileInput = document.querySelector('input[type="file"]'); fileInput.addEventListener('change', (event) => { const file = event.target.files[0]; const newFile = new File([file], 'newFileName.txt', { type: file.type }); // Now you can upload 'newFile' using FormData or other methods });
By following these patterns, you can effectively rename files in a Node.js environment or manipulate file references in a web browser context.
What is Basedash?
What is Basedash?
What is Basedash?
Ship faster, worry less with Basedash
Ship faster, worry less with Basedash
Ship faster, worry less with Basedash
You're busy enough with product work to be weighed down building, maintaining, scoping and developing internal apps and admin panels. Forget all of that, and give your team the admin panel that you don't have to build. Launch in less time than it takes to run a standup.
You're busy enough with product work to be weighed down building, maintaining, scoping and developing internal apps and admin panels. Forget all of that, and give your team the admin panel that you don't have to build. Launch in less time than it takes to run a standup.
You're busy enough with product work to be weighed down building, maintaining, scoping and developing internal apps and admin panels. Forget all of that, and give your team the admin panel that you don't have to build. Launch in less time than it takes to run a standup.
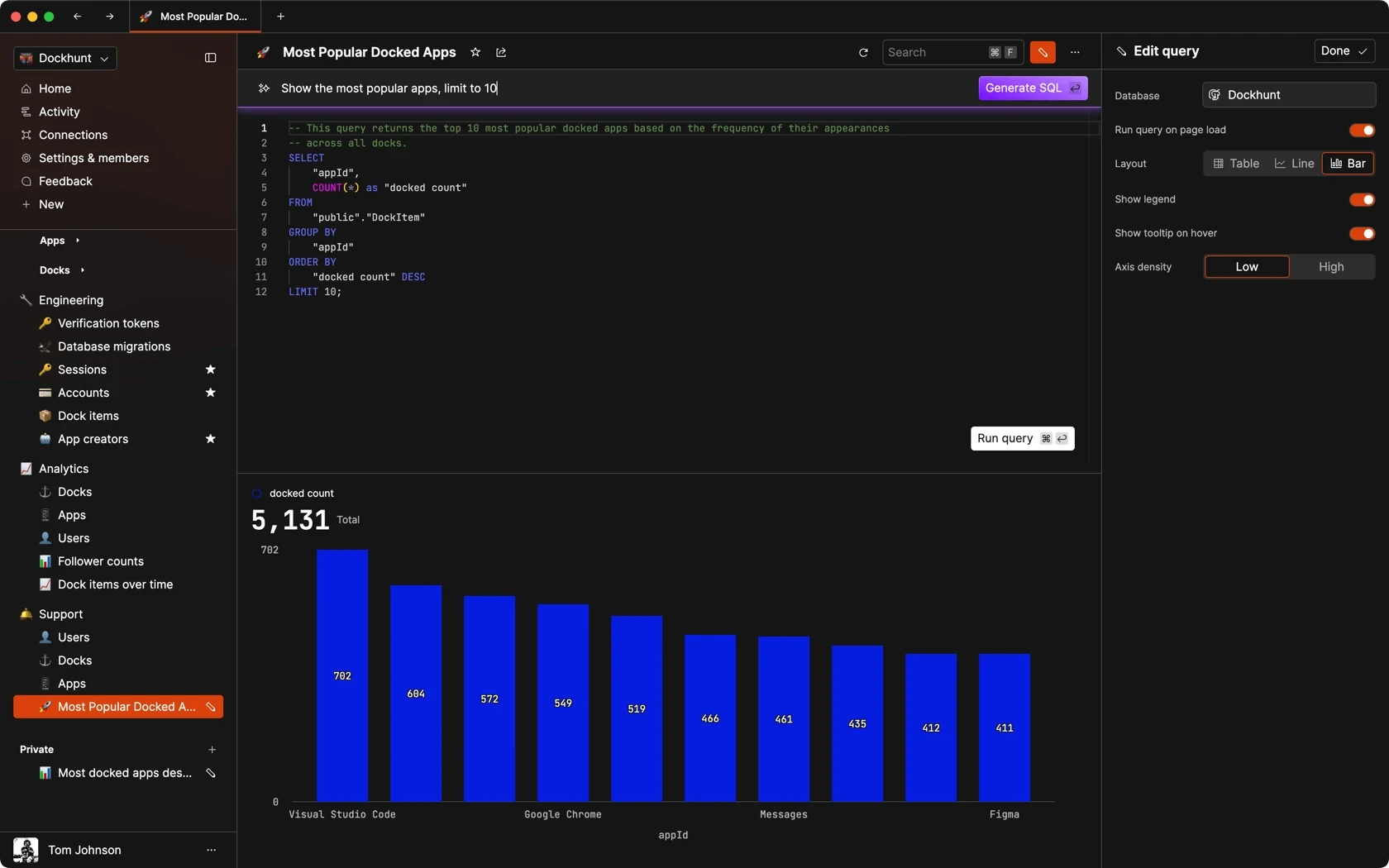
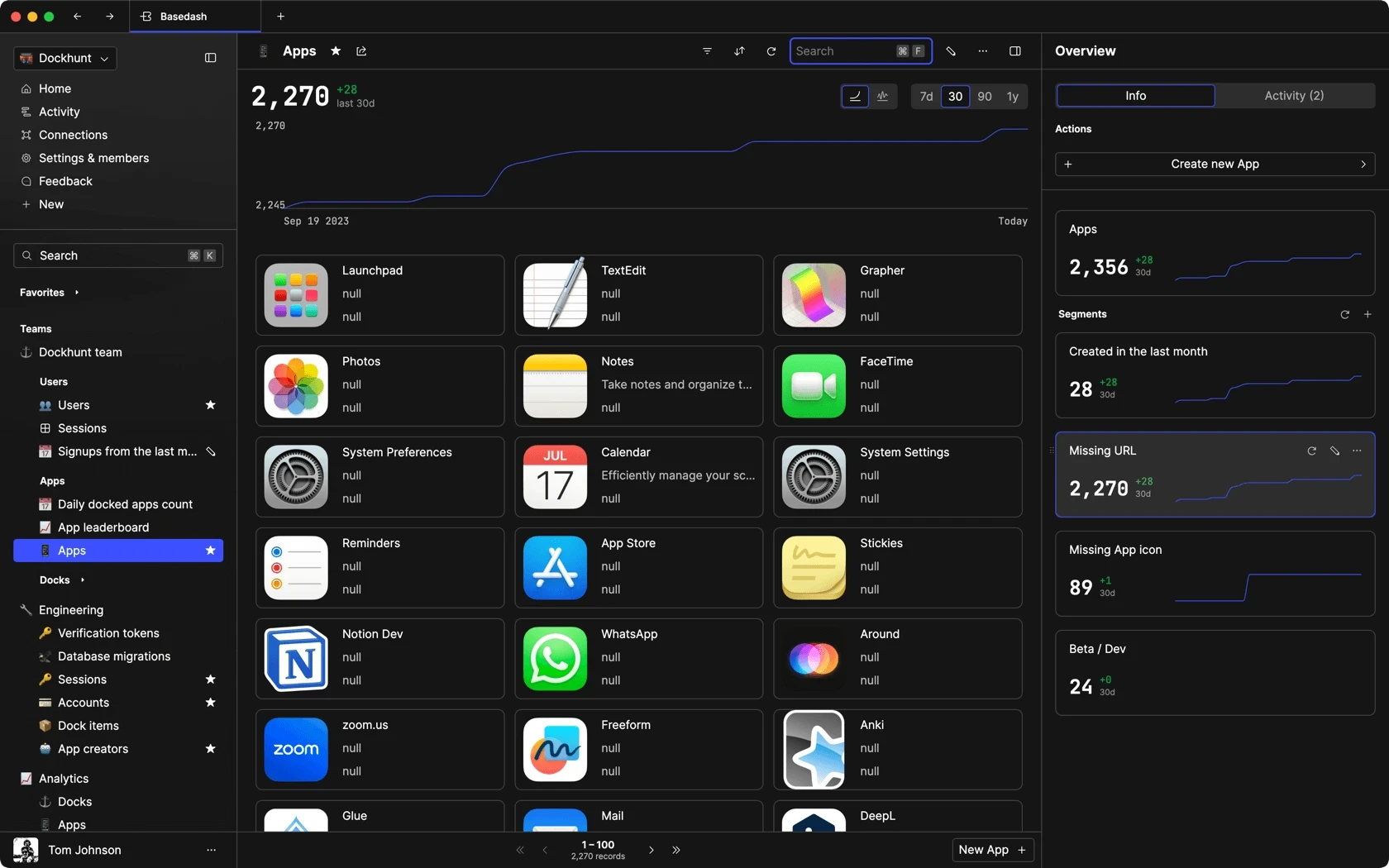
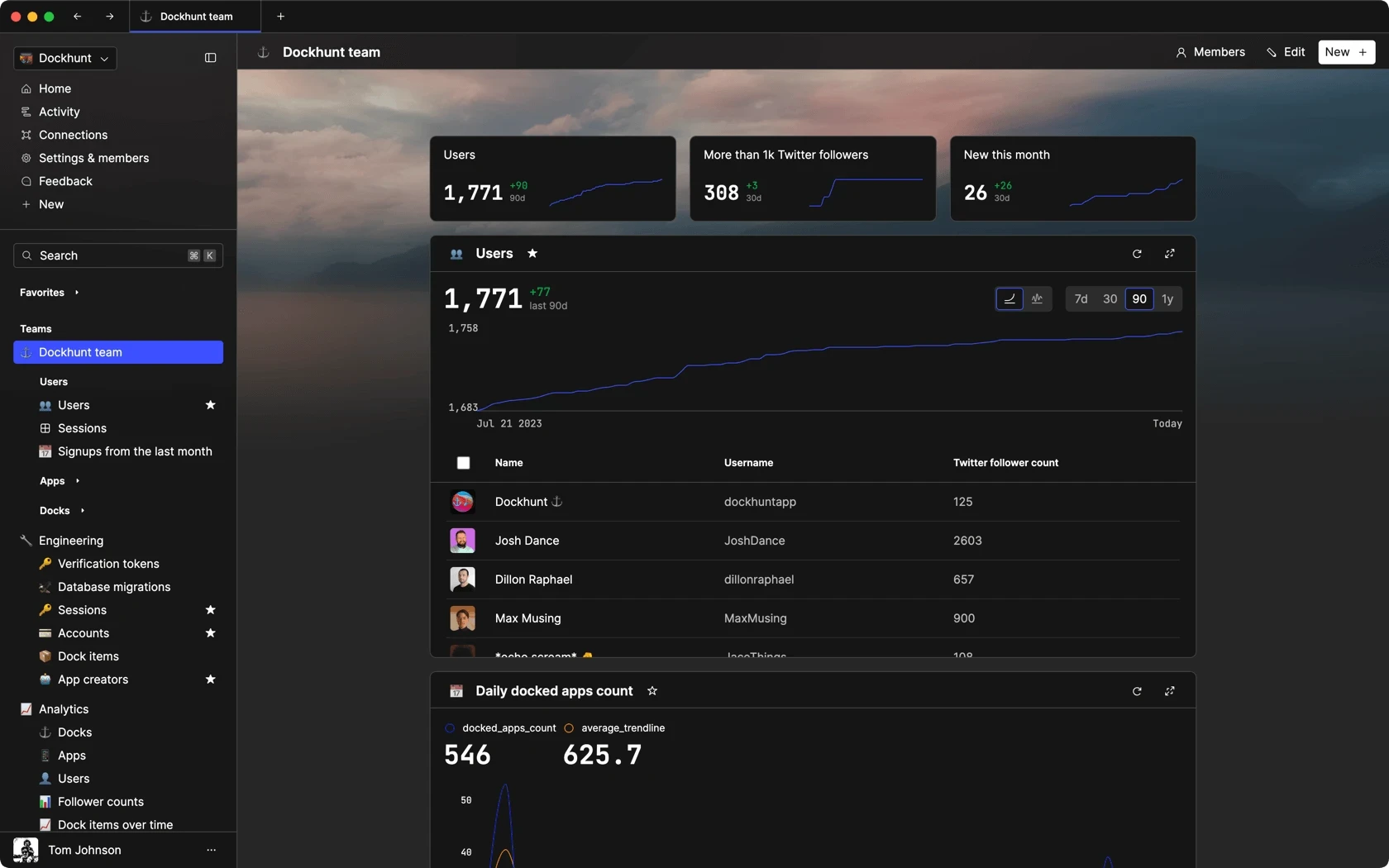
Dashboards and charts
Edit data, create records, oversee how your product is running without the need to build or manage custom software.
USER CRM
ADMIN PANEL
SQL COMPOSER WITH AI
Related posts
Related posts
Related posts



How to Remove Characters from a String in JavaScript
Jeremy Sarchet



How to Sort Strings in JavaScript
Max Musing



How to Remove Spaces from a String in JavaScript
Jeremy Sarchet



Detecting Prime Numbers in JavaScript
Robert Cooper



How to Parse Boolean Values in JavaScript
Max Musing



How to Remove a Substring from a String in JavaScript
Robert Cooper
