
What are Type Predicates in TypeScript?
October 29, 2023
TypeScript, a statically typed superset of JavaScript, introduces a myriad of features to help developers write safe and self-documenting code. One such feature is the "type predicate". This guide will delve into what type predicates are, why they're useful, and how to use them.
What's a Type Predicate?
A type predicate is a function whose return type is a boolean value that's used to narrow down types. They come handy when TypeScript can't automatically infer the type of a variable or when more sophisticated type checks are needed.
The syntax for a type predicate function is:
function isOfType(arg: any): arg is Type { // ... logic }
The arg is Type syntax is the actual type predicate. It's signaling to TypeScript that, when the function returns true, the caller can be certain that arg is of type Type.
Why Are They Useful?
Consider scenarios where you have a union type (e.g., string | number) and you want to run different code based on the type. The standard way is to use type guards:
function processInput(input: string | number) { if (typeof input === 'string') { console.log(input.toUpperCase()); } else { console.log(input.toFixed(2)); } }
While typeof and instanceof are useful, they don't cover all cases. Enter type predicates. They allow developers to create custom type guards that narrow types based on bespoke logic.
You could ship faster.
Imagine the time you'd save if you never had to build another internal tool, write a SQL report, or manage another admin panel again. Basedash is built by internal tool builders, for internal tool builders. Our mission is to change the way developers work, so you can focus on building your product.

Examples of Using Type Predicates
1. With Interfaces
Imagine you have two interfaces, Cat and Dog, and you want to check if an animal is a Cat:
interface Cat { purr(): void; } interface Dog { bark(): void; } function isCat(animal: Cat | Dog): animal is Cat { return (animal as Cat).purr !== undefined; }
Now, whenever you use isCat in a conditional, TypeScript knows the type:
const myPet: Cat | Dog = getPetSomehow(); if (isCat(myPet)) { myPet.purr(); // TypeScript knows `myPet` is a `Cat` here. } else { myPet.bark(); }
2. With Classes
Similarly, you can use type predicates with classes:
class Bird { fly() { /*...*/ } } class Fish { swim() { /*...*/ } } function isBird(pet: Bird | Fish): pet is Bird { return (pet as Bird).fly !== undefined; }
Caveats
- Ensure Accuracy: The logic inside your type predicate must be accurate. If the logic claims an instance is of a specific type when it's not, it could lead to runtime errors.
- TypeScript's Trust: Once the type predicate function returns
true, TypeScript completely trusts that the type is narrowed. It doesn't double-check, so make sure your predicates are correct. - No Direct Output: The main aim of type predicates isn't to return a boolean for the developer to use, but rather to provide type information to TypeScript. They're primarily for type checking and not for runtime checks.
Recap
- A type predicate is a function that narrows types based on its return value.
- The syntax for a type predicate is
arg is Type. - They're especially useful when working with union types or when
typeofandinstanceofaren't sufficient. - Always ensure that the logic in the type predicate function is accurate to avoid potential runtime errors.
TOC
October 29, 2023
TypeScript, a statically typed superset of JavaScript, introduces a myriad of features to help developers write safe and self-documenting code. One such feature is the "type predicate". This guide will delve into what type predicates are, why they're useful, and how to use them.
What's a Type Predicate?
A type predicate is a function whose return type is a boolean value that's used to narrow down types. They come handy when TypeScript can't automatically infer the type of a variable or when more sophisticated type checks are needed.
The syntax for a type predicate function is:
function isOfType(arg: any): arg is Type { // ... logic }
The arg is Type syntax is the actual type predicate. It's signaling to TypeScript that, when the function returns true, the caller can be certain that arg is of type Type.
Why Are They Useful?
Consider scenarios where you have a union type (e.g., string | number) and you want to run different code based on the type. The standard way is to use type guards:
function processInput(input: string | number) { if (typeof input === 'string') { console.log(input.toUpperCase()); } else { console.log(input.toFixed(2)); } }
While typeof and instanceof are useful, they don't cover all cases. Enter type predicates. They allow developers to create custom type guards that narrow types based on bespoke logic.
You could ship faster.
Imagine the time you'd save if you never had to build another internal tool, write a SQL report, or manage another admin panel again. Basedash is built by internal tool builders, for internal tool builders. Our mission is to change the way developers work, so you can focus on building your product.

Examples of Using Type Predicates
1. With Interfaces
Imagine you have two interfaces, Cat and Dog, and you want to check if an animal is a Cat:
interface Cat { purr(): void; } interface Dog { bark(): void; } function isCat(animal: Cat | Dog): animal is Cat { return (animal as Cat).purr !== undefined; }
Now, whenever you use isCat in a conditional, TypeScript knows the type:
const myPet: Cat | Dog = getPetSomehow(); if (isCat(myPet)) { myPet.purr(); // TypeScript knows `myPet` is a `Cat` here. } else { myPet.bark(); }
2. With Classes
Similarly, you can use type predicates with classes:
class Bird { fly() { /*...*/ } } class Fish { swim() { /*...*/ } } function isBird(pet: Bird | Fish): pet is Bird { return (pet as Bird).fly !== undefined; }
Caveats
- Ensure Accuracy: The logic inside your type predicate must be accurate. If the logic claims an instance is of a specific type when it's not, it could lead to runtime errors.
- TypeScript's Trust: Once the type predicate function returns
true, TypeScript completely trusts that the type is narrowed. It doesn't double-check, so make sure your predicates are correct. - No Direct Output: The main aim of type predicates isn't to return a boolean for the developer to use, but rather to provide type information to TypeScript. They're primarily for type checking and not for runtime checks.
Recap
- A type predicate is a function that narrows types based on its return value.
- The syntax for a type predicate is
arg is Type. - They're especially useful when working with union types or when
typeofandinstanceofaren't sufficient. - Always ensure that the logic in the type predicate function is accurate to avoid potential runtime errors.
October 29, 2023
TypeScript, a statically typed superset of JavaScript, introduces a myriad of features to help developers write safe and self-documenting code. One such feature is the "type predicate". This guide will delve into what type predicates are, why they're useful, and how to use them.
What's a Type Predicate?
A type predicate is a function whose return type is a boolean value that's used to narrow down types. They come handy when TypeScript can't automatically infer the type of a variable or when more sophisticated type checks are needed.
The syntax for a type predicate function is:
function isOfType(arg: any): arg is Type { // ... logic }
The arg is Type syntax is the actual type predicate. It's signaling to TypeScript that, when the function returns true, the caller can be certain that arg is of type Type.
Why Are They Useful?
Consider scenarios where you have a union type (e.g., string | number) and you want to run different code based on the type. The standard way is to use type guards:
function processInput(input: string | number) { if (typeof input === 'string') { console.log(input.toUpperCase()); } else { console.log(input.toFixed(2)); } }
While typeof and instanceof are useful, they don't cover all cases. Enter type predicates. They allow developers to create custom type guards that narrow types based on bespoke logic.
You could ship faster.
Imagine the time you'd save if you never had to build another internal tool, write a SQL report, or manage another admin panel again. Basedash is built by internal tool builders, for internal tool builders. Our mission is to change the way developers work, so you can focus on building your product.

Examples of Using Type Predicates
1. With Interfaces
Imagine you have two interfaces, Cat and Dog, and you want to check if an animal is a Cat:
interface Cat { purr(): void; } interface Dog { bark(): void; } function isCat(animal: Cat | Dog): animal is Cat { return (animal as Cat).purr !== undefined; }
Now, whenever you use isCat in a conditional, TypeScript knows the type:
const myPet: Cat | Dog = getPetSomehow(); if (isCat(myPet)) { myPet.purr(); // TypeScript knows `myPet` is a `Cat` here. } else { myPet.bark(); }
2. With Classes
Similarly, you can use type predicates with classes:
class Bird { fly() { /*...*/ } } class Fish { swim() { /*...*/ } } function isBird(pet: Bird | Fish): pet is Bird { return (pet as Bird).fly !== undefined; }
Caveats
- Ensure Accuracy: The logic inside your type predicate must be accurate. If the logic claims an instance is of a specific type when it's not, it could lead to runtime errors.
- TypeScript's Trust: Once the type predicate function returns
true, TypeScript completely trusts that the type is narrowed. It doesn't double-check, so make sure your predicates are correct. - No Direct Output: The main aim of type predicates isn't to return a boolean for the developer to use, but rather to provide type information to TypeScript. They're primarily for type checking and not for runtime checks.
Recap
- A type predicate is a function that narrows types based on its return value.
- The syntax for a type predicate is
arg is Type. - They're especially useful when working with union types or when
typeofandinstanceofaren't sufficient. - Always ensure that the logic in the type predicate function is accurate to avoid potential runtime errors.
What is Basedash?
What is Basedash?
What is Basedash?
Ship faster, worry less with Basedash
Ship faster, worry less with Basedash
Ship faster, worry less with Basedash
You're busy enough with product work to be weighed down building, maintaining, scoping and developing internal apps and admin panels. Forget all of that, and give your team the admin panel that you don't have to build. Launch in less time than it takes to run a standup.
You're busy enough with product work to be weighed down building, maintaining, scoping and developing internal apps and admin panels. Forget all of that, and give your team the admin panel that you don't have to build. Launch in less time than it takes to run a standup.
You're busy enough with product work to be weighed down building, maintaining, scoping and developing internal apps and admin panels. Forget all of that, and give your team the admin panel that you don't have to build. Launch in less time than it takes to run a standup.
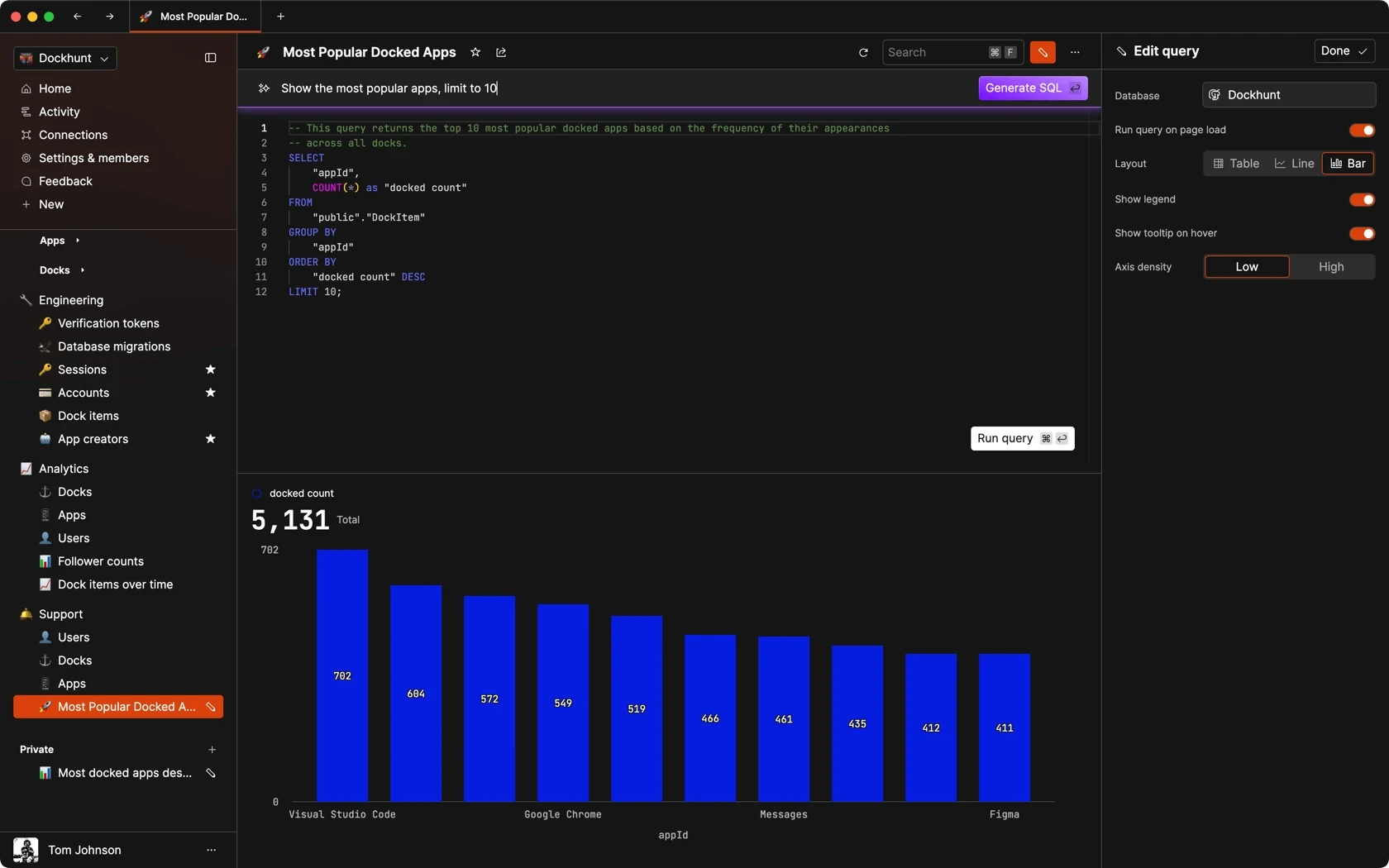
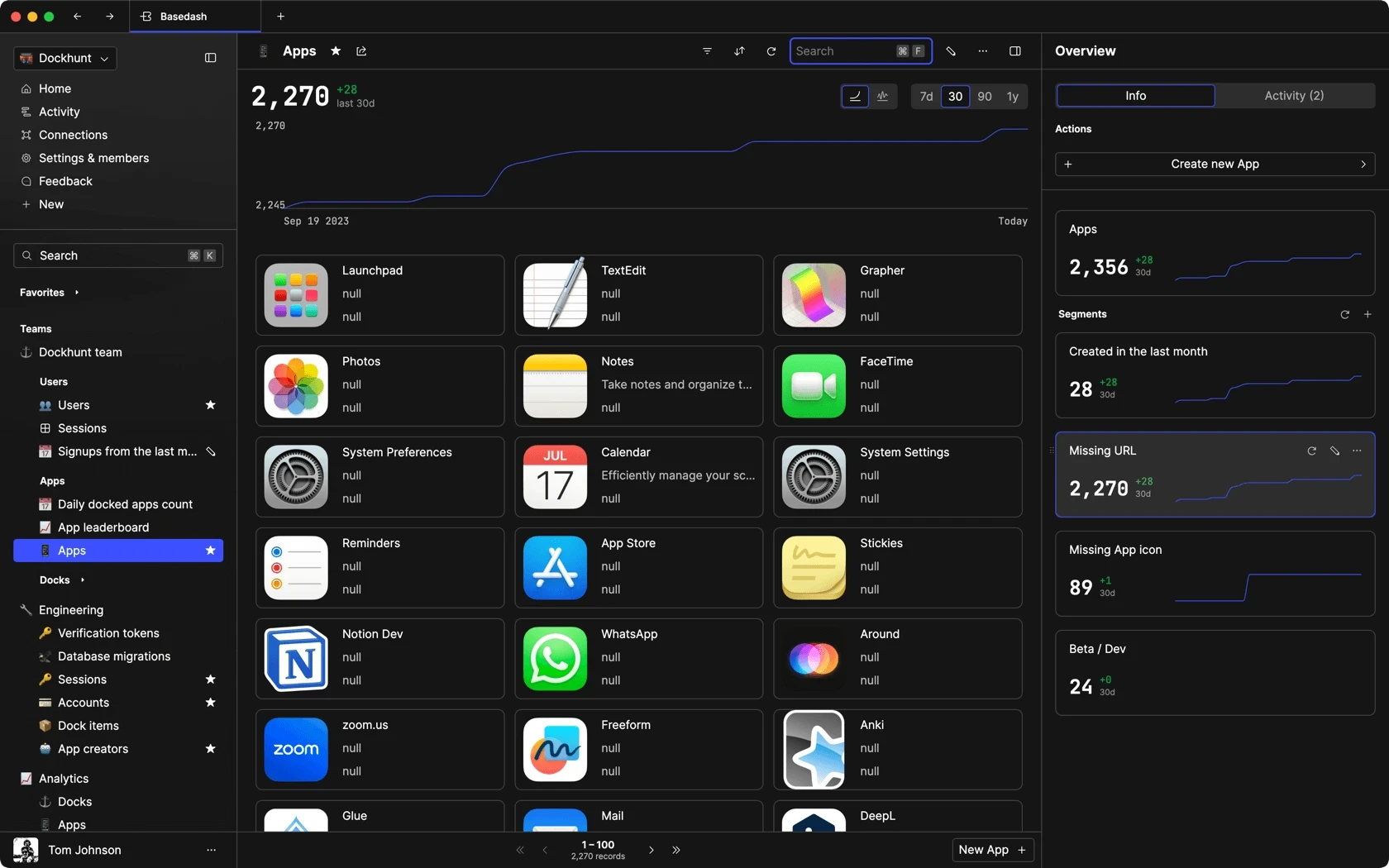
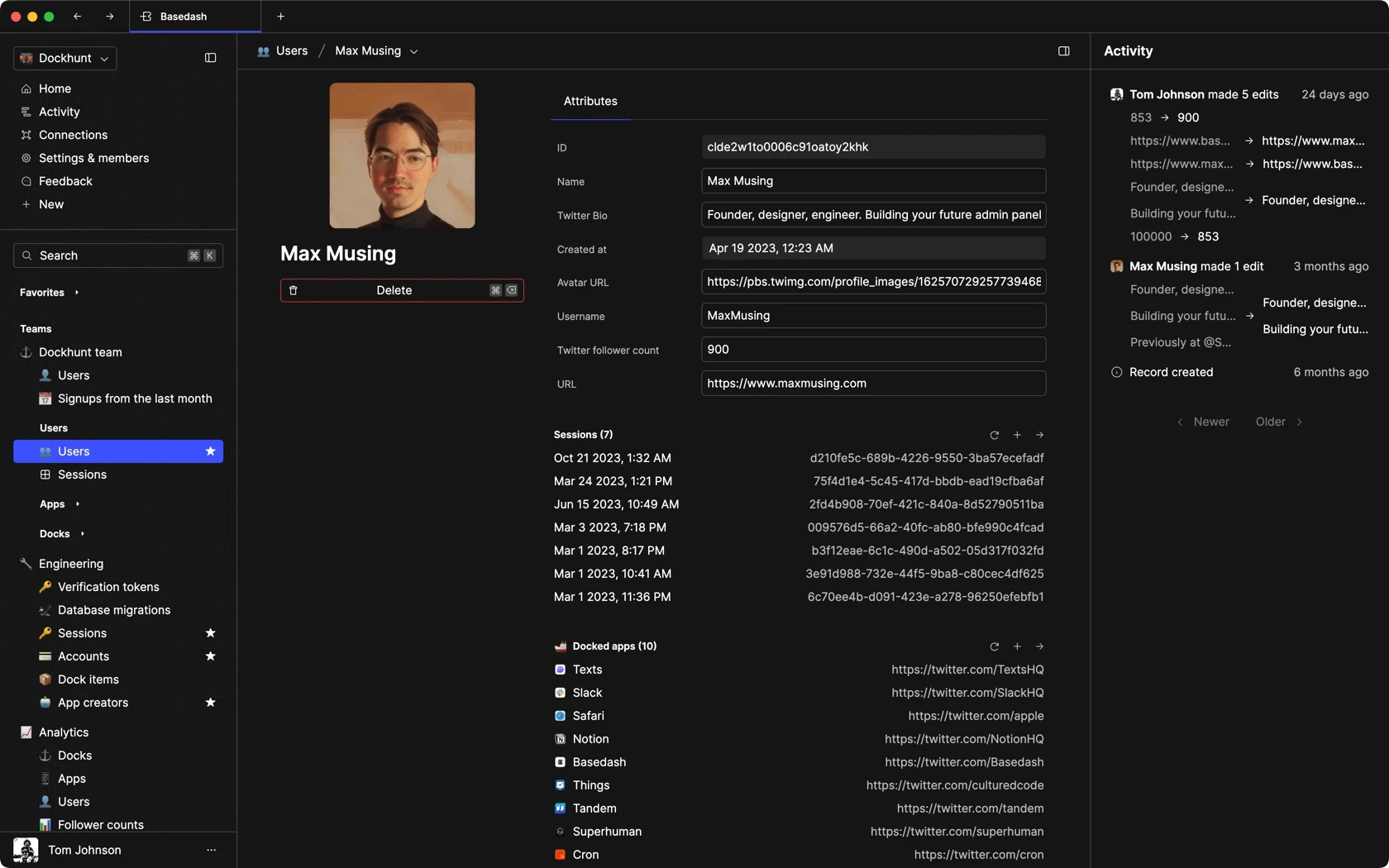
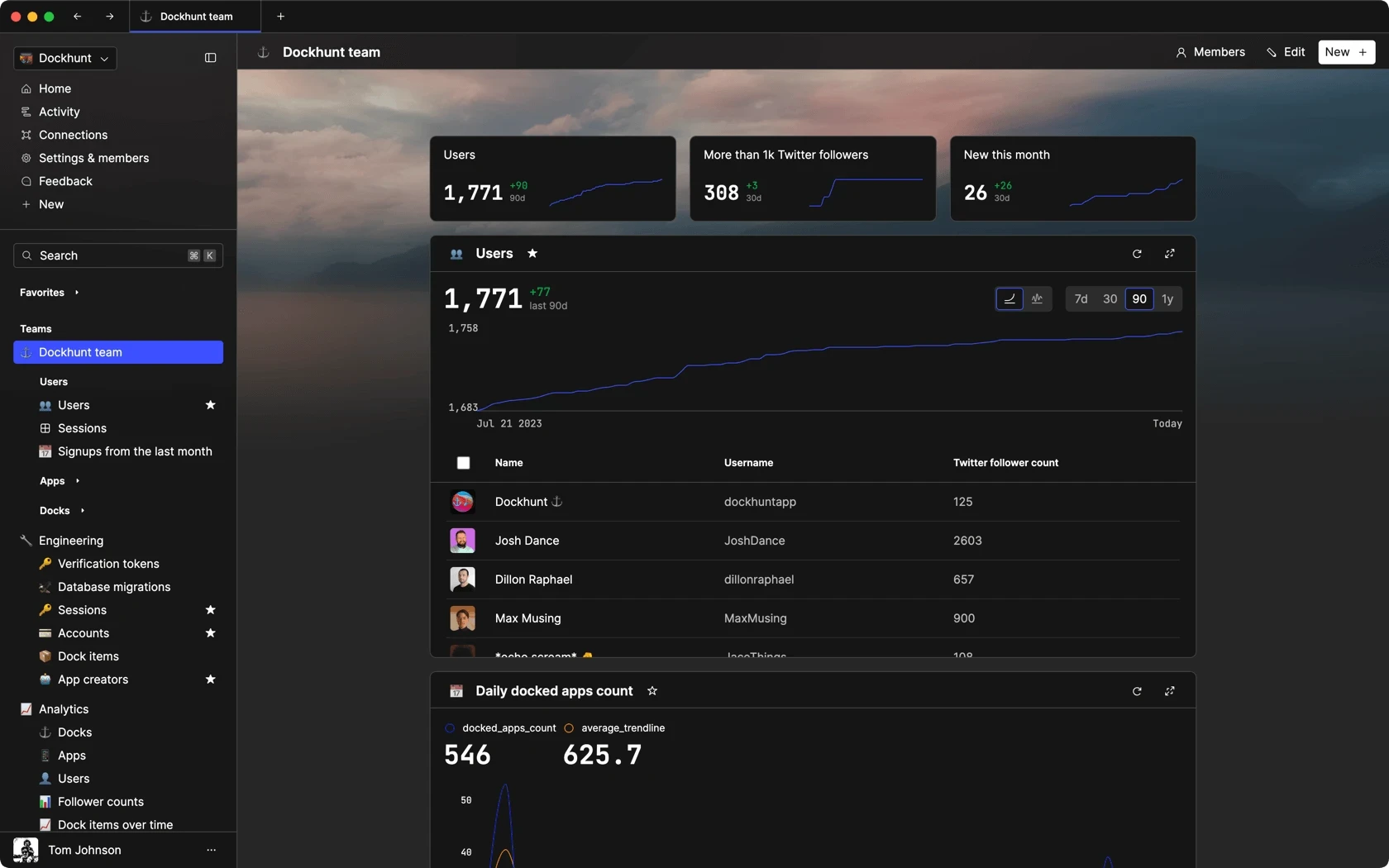
Dashboards and charts
Edit data, create records, oversee how your product is running without the need to build or manage custom software.
USER CRM
ADMIN PANEL
SQL COMPOSER WITH AI
Related posts
Related posts
Related posts



How to Remove Characters from a String in JavaScript
Jeremy Sarchet



How to Sort Strings in JavaScript
Max Musing



How to Remove Spaces from a String in JavaScript
Jeremy Sarchet



Detecting Prime Numbers in JavaScript
Robert Cooper



How to Parse Boolean Values in JavaScript
Max Musing



How to Remove a Substring from a String in JavaScript
Robert Cooper
