
How to Undo a Git Rebase
October 27, 2023
Whether you've rebased by accident, realized there was a mistake, or simply want to understand how to reverse a rebase operation, this guide has got you covered. Rebasing is a powerful tool, but like all powerful tools, it needs to be handled with care. Let's dive in and learn how to undo a git rebase.
The Simple Case: Interactive Rebasing
If you've just rebased and immediately realize your mistake, it's pretty straightforward to get back to where you were:
git reflog
reflog is a mechanism to record when the tip of branches are updated. This command will show you a list of the recent actions you've taken in your repo. You should see an entry like HEAD@{n}: rebase (start): checkout <commit_hash>.
To return to the state before the rebase, identify the commit hash you want to go back to and use:
git reset --hard HEAD@{n}
Replace {n} with the appropriate number from the reflog.
Undoing After Pushing
If you've pushed your rebased branch to a remote, things get trickier, especially if other people have pulled the rebased branch. If you're working alone or you're certain no one else has pulled the changes:
- Use the
reflogas mentioned above to get back to the desired state. - Push the branch with the
-forceflag:
git push origin <branch_name> --force
Warning: Force pushing can be dangerous as it overwrites changes in the remote branch. Always communicate with your team before force pushing to avoid unexpected issues.
You could ship faster.
Imagine the time you'd save if you never had to build another internal tool, write a SQL report, or manage another admin panel again. Basedash is built by internal tool builders, for internal tool builders. Our mission is to change the way developers work, so you can focus on building your product.

Using git revert
If you can't use the reflog for some reason or you've pushed your changes and other people have based work on it, you might consider using git revert. Instead of truly "undoing", this command creates new commits that reverse the effects of previous commits. This way, you aren't rewriting commit history:
git revert OLDEST_COMMIT^..NEWEST_COMMIT
This will create a new commit that undoes the changes between the oldest and newest commits of the rebase.
Manual Undo
If none of the above methods work or you want to be more hands-on, you can manually checkout to the commit before the rebase and create a new branch:
git checkout <commit_hash_before_rebase> git checkout -b new_branch_name
From here, you can manually re-apply the changes you want, commit by commit, and leave out the ones you don't.
Tips and Reminders
- Always backup your branch before doing a rebase. It's as simple as creating a duplicate branch:
git branch backup_branch_name. - Be cautious about rebasing branches that have been pushed to a public repository, especially if other developers are collaborating on that branch. It can create inconsistencies and confusion.
- Communication is key. If working with a team, always coordinate with team members about major git operations to avoid disruption and loss of work.
Remember, Git is designed to be flexible and forgiving. Even if you make a mistake, there's almost always a way to recover or correct it. Happy coding!
TOC
October 27, 2023
Whether you've rebased by accident, realized there was a mistake, or simply want to understand how to reverse a rebase operation, this guide has got you covered. Rebasing is a powerful tool, but like all powerful tools, it needs to be handled with care. Let's dive in and learn how to undo a git rebase.
The Simple Case: Interactive Rebasing
If you've just rebased and immediately realize your mistake, it's pretty straightforward to get back to where you were:
git reflog
reflog is a mechanism to record when the tip of branches are updated. This command will show you a list of the recent actions you've taken in your repo. You should see an entry like HEAD@{n}: rebase (start): checkout <commit_hash>.
To return to the state before the rebase, identify the commit hash you want to go back to and use:
git reset --hard HEAD@{n}
Replace {n} with the appropriate number from the reflog.
Undoing After Pushing
If you've pushed your rebased branch to a remote, things get trickier, especially if other people have pulled the rebased branch. If you're working alone or you're certain no one else has pulled the changes:
- Use the
reflogas mentioned above to get back to the desired state. - Push the branch with the
-forceflag:
git push origin <branch_name> --force
Warning: Force pushing can be dangerous as it overwrites changes in the remote branch. Always communicate with your team before force pushing to avoid unexpected issues.
You could ship faster.
Imagine the time you'd save if you never had to build another internal tool, write a SQL report, or manage another admin panel again. Basedash is built by internal tool builders, for internal tool builders. Our mission is to change the way developers work, so you can focus on building your product.

Using git revert
If you can't use the reflog for some reason or you've pushed your changes and other people have based work on it, you might consider using git revert. Instead of truly "undoing", this command creates new commits that reverse the effects of previous commits. This way, you aren't rewriting commit history:
git revert OLDEST_COMMIT^..NEWEST_COMMIT
This will create a new commit that undoes the changes between the oldest and newest commits of the rebase.
Manual Undo
If none of the above methods work or you want to be more hands-on, you can manually checkout to the commit before the rebase and create a new branch:
git checkout <commit_hash_before_rebase> git checkout -b new_branch_name
From here, you can manually re-apply the changes you want, commit by commit, and leave out the ones you don't.
Tips and Reminders
- Always backup your branch before doing a rebase. It's as simple as creating a duplicate branch:
git branch backup_branch_name. - Be cautious about rebasing branches that have been pushed to a public repository, especially if other developers are collaborating on that branch. It can create inconsistencies and confusion.
- Communication is key. If working with a team, always coordinate with team members about major git operations to avoid disruption and loss of work.
Remember, Git is designed to be flexible and forgiving. Even if you make a mistake, there's almost always a way to recover or correct it. Happy coding!
October 27, 2023
Whether you've rebased by accident, realized there was a mistake, or simply want to understand how to reverse a rebase operation, this guide has got you covered. Rebasing is a powerful tool, but like all powerful tools, it needs to be handled with care. Let's dive in and learn how to undo a git rebase.
The Simple Case: Interactive Rebasing
If you've just rebased and immediately realize your mistake, it's pretty straightforward to get back to where you were:
git reflog
reflog is a mechanism to record when the tip of branches are updated. This command will show you a list of the recent actions you've taken in your repo. You should see an entry like HEAD@{n}: rebase (start): checkout <commit_hash>.
To return to the state before the rebase, identify the commit hash you want to go back to and use:
git reset --hard HEAD@{n}
Replace {n} with the appropriate number from the reflog.
Undoing After Pushing
If you've pushed your rebased branch to a remote, things get trickier, especially if other people have pulled the rebased branch. If you're working alone or you're certain no one else has pulled the changes:
- Use the
reflogas mentioned above to get back to the desired state. - Push the branch with the
-forceflag:
git push origin <branch_name> --force
Warning: Force pushing can be dangerous as it overwrites changes in the remote branch. Always communicate with your team before force pushing to avoid unexpected issues.
You could ship faster.
Imagine the time you'd save if you never had to build another internal tool, write a SQL report, or manage another admin panel again. Basedash is built by internal tool builders, for internal tool builders. Our mission is to change the way developers work, so you can focus on building your product.

Using git revert
If you can't use the reflog for some reason or you've pushed your changes and other people have based work on it, you might consider using git revert. Instead of truly "undoing", this command creates new commits that reverse the effects of previous commits. This way, you aren't rewriting commit history:
git revert OLDEST_COMMIT^..NEWEST_COMMIT
This will create a new commit that undoes the changes between the oldest and newest commits of the rebase.
Manual Undo
If none of the above methods work or you want to be more hands-on, you can manually checkout to the commit before the rebase and create a new branch:
git checkout <commit_hash_before_rebase> git checkout -b new_branch_name
From here, you can manually re-apply the changes you want, commit by commit, and leave out the ones you don't.
Tips and Reminders
- Always backup your branch before doing a rebase. It's as simple as creating a duplicate branch:
git branch backup_branch_name. - Be cautious about rebasing branches that have been pushed to a public repository, especially if other developers are collaborating on that branch. It can create inconsistencies and confusion.
- Communication is key. If working with a team, always coordinate with team members about major git operations to avoid disruption and loss of work.
Remember, Git is designed to be flexible and forgiving. Even if you make a mistake, there's almost always a way to recover or correct it. Happy coding!
What is Basedash?
What is Basedash?
What is Basedash?
Ship faster, worry less with Basedash
Ship faster, worry less with Basedash
Ship faster, worry less with Basedash
You're busy enough with product work to be weighed down building, maintaining, scoping and developing internal apps and admin panels. Forget all of that, and give your team the admin panel that you don't have to build. Launch in less time than it takes to run a standup.
You're busy enough with product work to be weighed down building, maintaining, scoping and developing internal apps and admin panels. Forget all of that, and give your team the admin panel that you don't have to build. Launch in less time than it takes to run a standup.
You're busy enough with product work to be weighed down building, maintaining, scoping and developing internal apps and admin panels. Forget all of that, and give your team the admin panel that you don't have to build. Launch in less time than it takes to run a standup.
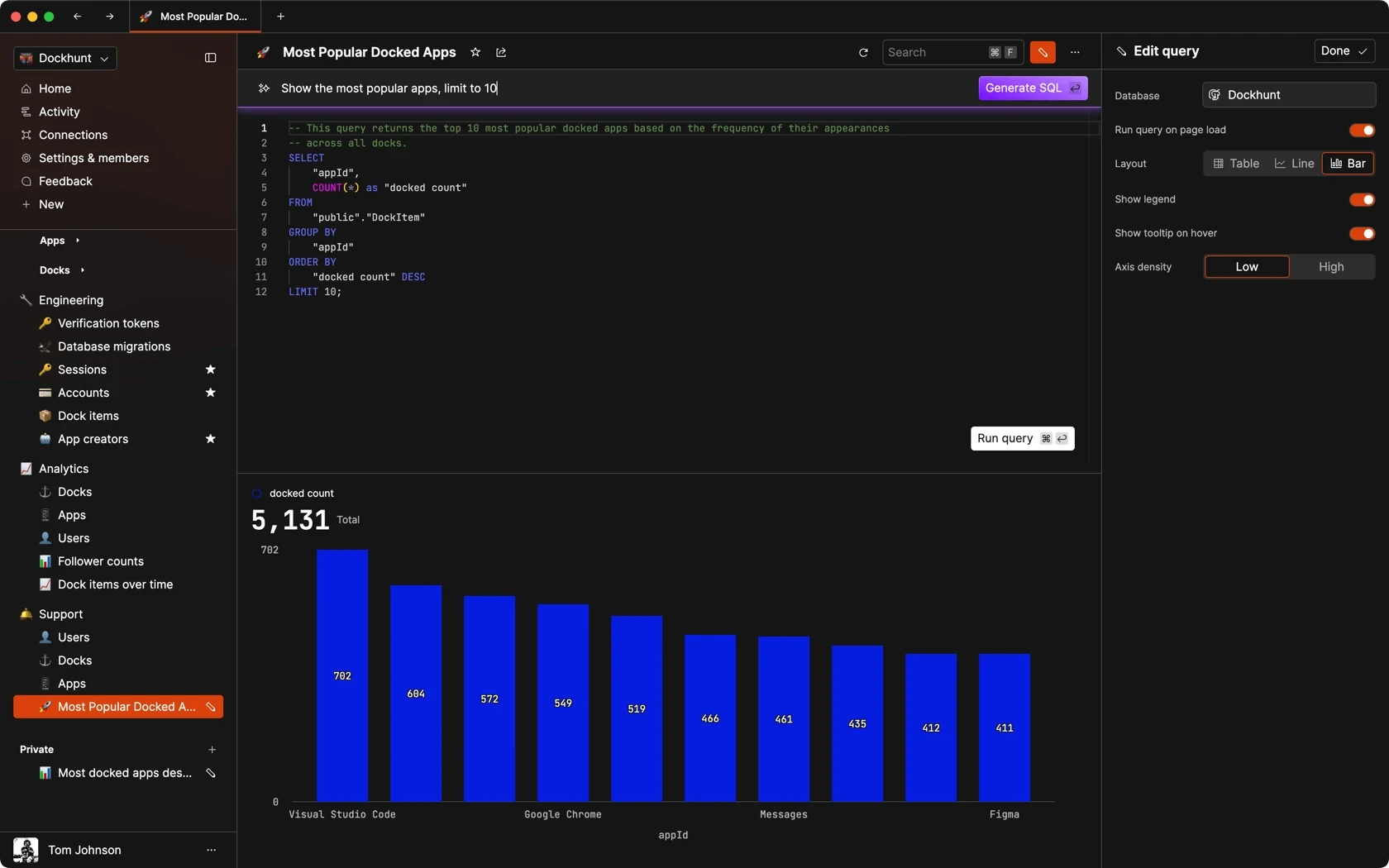
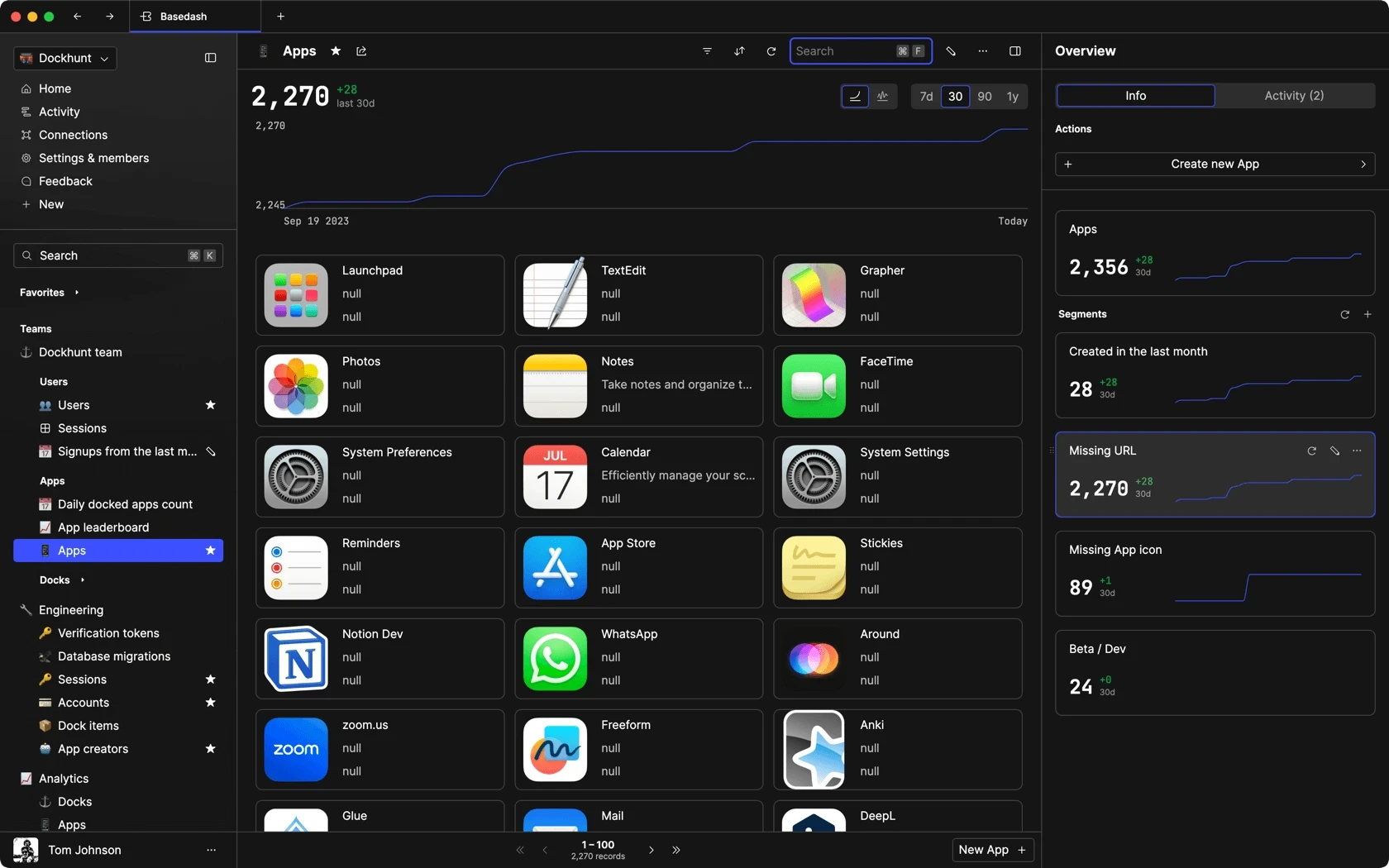
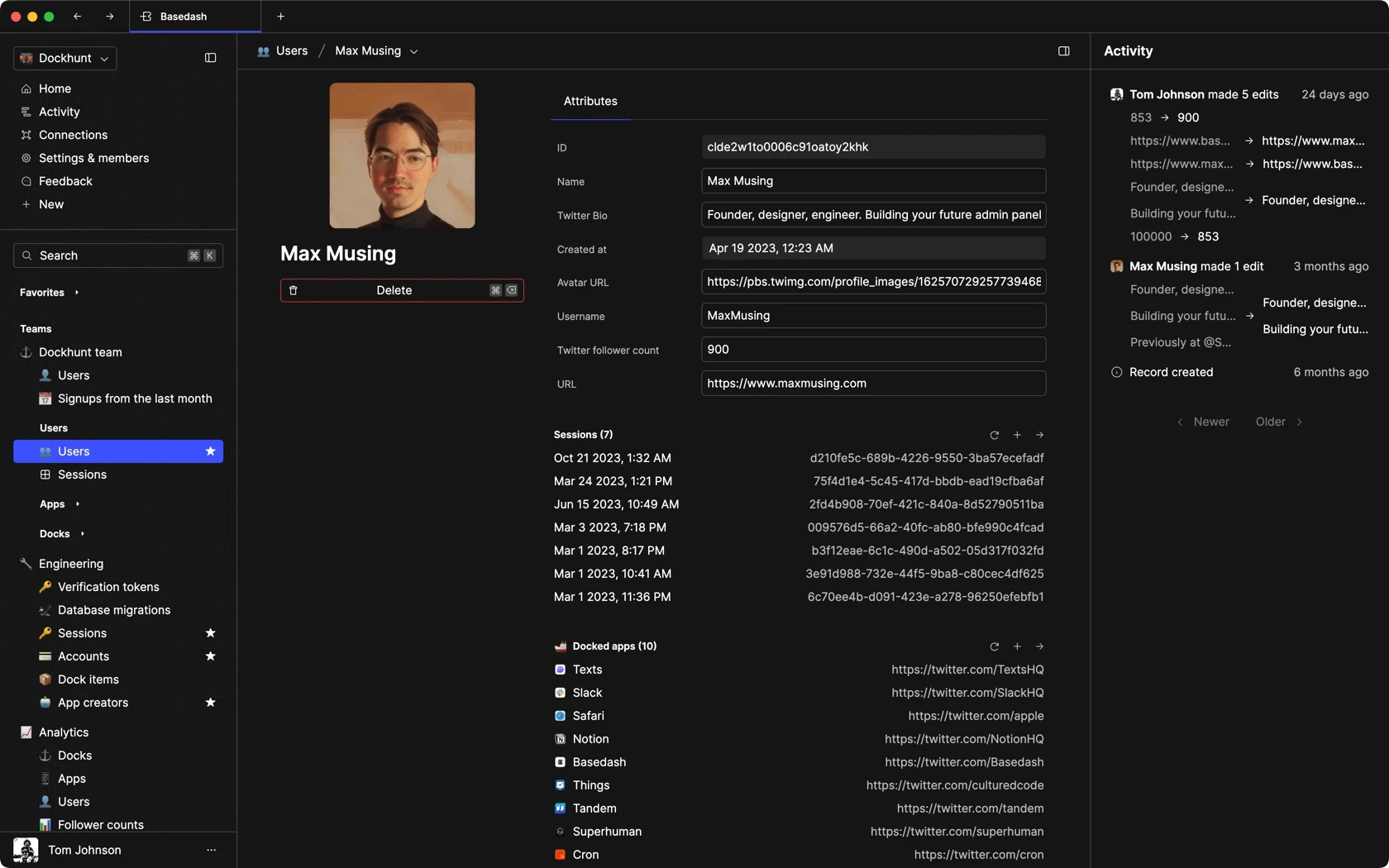
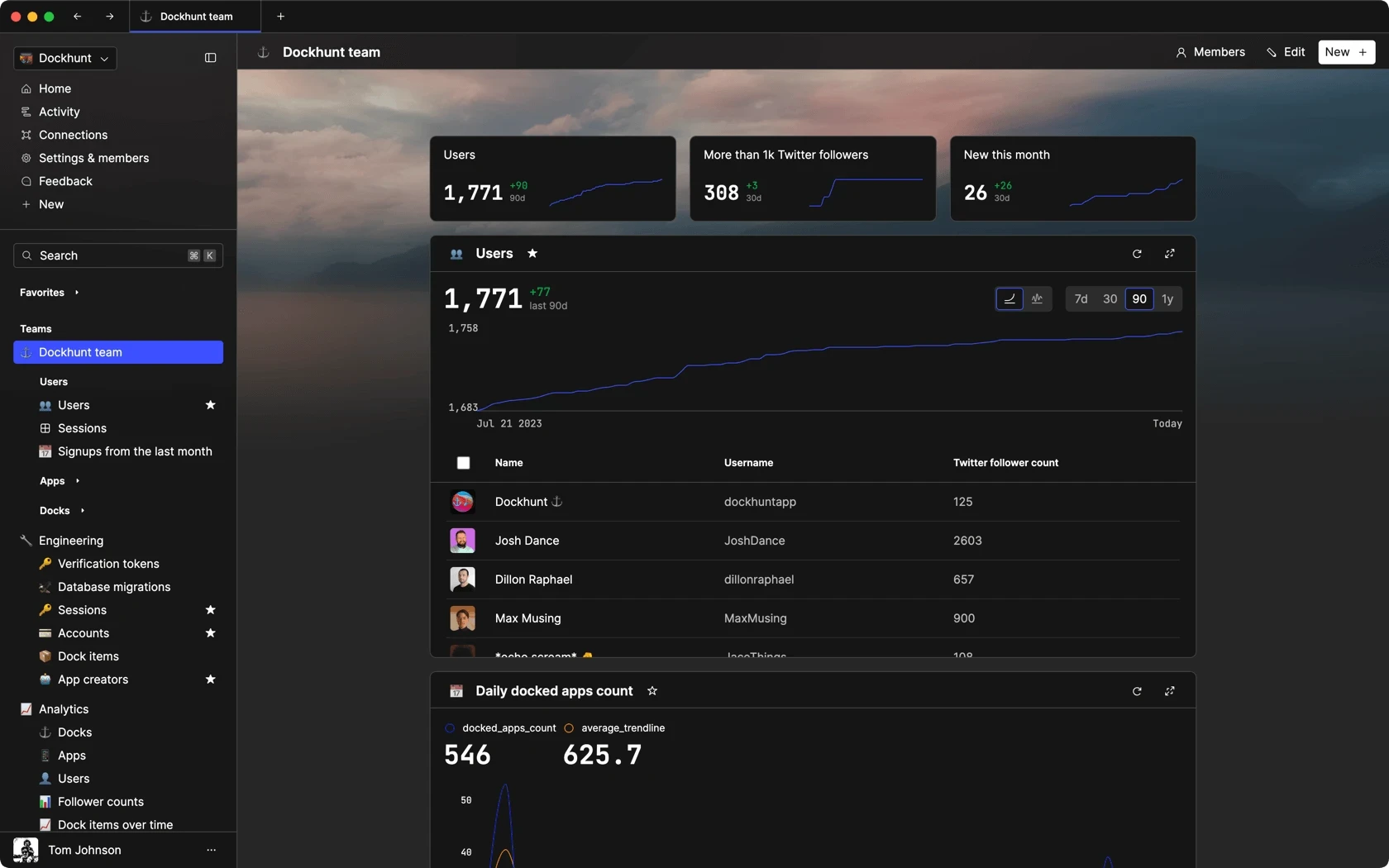
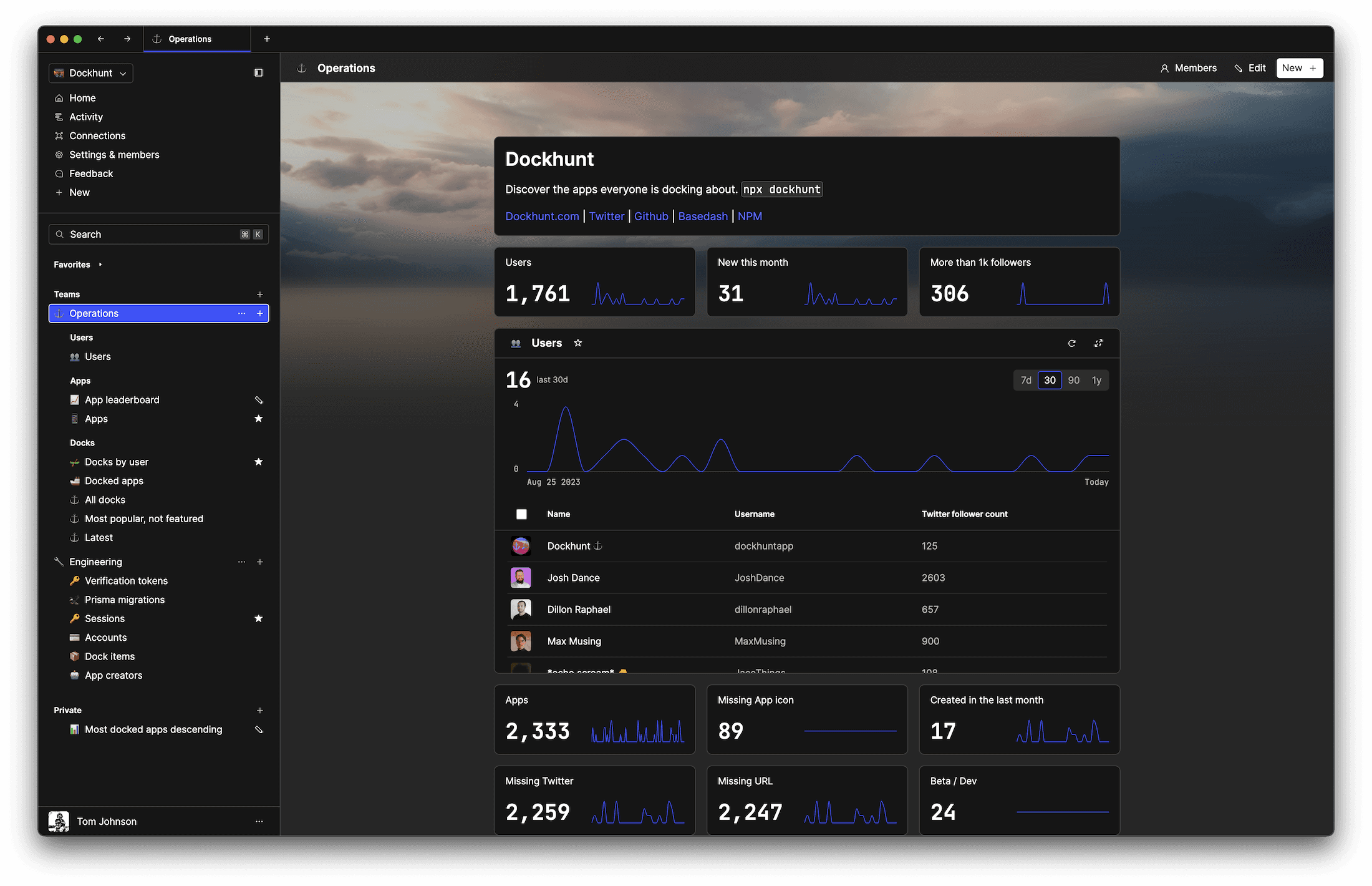
Dashboards and charts
Edit data, create records, oversee how your product is running without the need to build or manage custom software.
USER CRM
ADMIN PANEL
SQL COMPOSER WITH AI
Related posts
Related posts
Related posts



How to Center a Table in HTML with CSS
Jeremy Sarchet


Adjusting HTML Table Column Width for Better Design
Robert Cooper



How to Link Multiple CSS Stylesheets in HTML
Robert Cooper



Mastering HTML Table Inline Styling: A Guide
Max Musing



HTML Multiple Style Attributes: A Quick Guide
Max Musing



How to Set HTML Table Width for Responsive Design
Max Musing
